Complete Health Indicator Report of Obesity Among Adults
Definition
Percentage of respondents aged 18 years and older who have a body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m^2^ calculated from self-reported weight and height.Numerator
Number of respondents aged 18 years and older who have a body mass index (BMI) greater than or equal to 30.0 kg/m^2^ calculated from self-reported weight and height.Denominator
Number of respondents aged 18 years and older for whom BMI can be calculated from their self-reported weight and height (excludes unknowns or refusals for weight and height).Data Interpretation Issues
Height and weight are self-reported and are subject to being misreported. To reduce bias and more accurately represent population data, the BRFSS has changed survey methodology. In 2010, it began conducting surveys by cellular phone in addition to landline phones. It also adopted "iterative proportional fitting" (raking) as its weighting method. More details about these changes can be found at: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/pdf/opha/resource/brfss/RakingImpact2011.pdf/ Raking Fact Sheet 2011].Why Is This Important?
Obesity can be costly and serious. Adults who are obese have an increased risk of hypertension, high LDL cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, stroke, and osteoarthritis.Healthy People Objective NWS-9:
Reduce the proportion of adults who are obeseU.S. Target: 30.5 percent
State Target: 24.0 percent
Other Objectives
The new U.S. Healthy People 2030 objective is Nutrition and Weight Status 03 (NWS-03): Reduce the proportion of adults with obesity. The U.S. target has been set for 36.0 percent of adults aged 20 or over. Data Source: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), CDC/NCHS See [https://health.gov/healthypeople/objectives-and-data/browse-objectives/overweight-and-obesity/reduce-proportion-adults-obesity-nws-03/ HealthyPeople 2030].How Are We Doing?
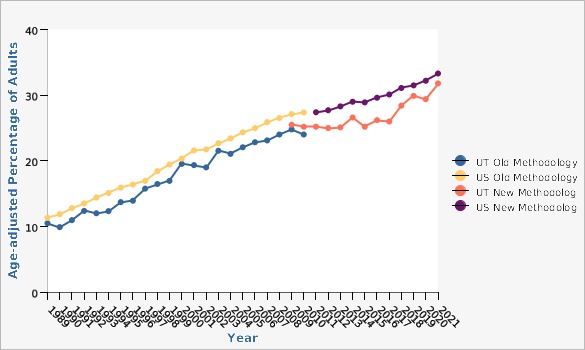
The age-adjusted percentage of Utah adults (18+) who were obese increased from 19.5% in 2000 to 31.8% in 2021. Nevertheless, Utah still has a lower obesity rate than most states. A release from CDC (2022) maps prevalence by state. See [http://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/prevalence-maps.html/ Adult Obesity Prevalence Maps].How Do We Compare With the U.S.?
The age-adjusted prevalence of obesity in Utah adults is slightly lower than the U.S. In 2021, the obesity prevalence rate in Utah adults was 31.8%, while the prevalence for U.S. adults was 33.3% (18+).What Is Being Done?
The Utah Department of Health and Human Service's Healthy Environments Active Living (HEAL) Program plays a key role in improving the health of residents in the state of Utah. The program was formed in July 2013 (as Healthy Living through Environment, Policy, and Improved Clinical Care: EPICC), through a new funding opportunity from the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that allowed for the merging of three previously existing programs: the Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Program, the Diabetes Prevention and Control Program, and the Physical Activity, Nutrition and Obesity Program, as well as the addition of a school health program. HEAL was recently restructured as part of a strategic planning process and the new program model focuses on staff and partners working together to address the social determinants of health while advancing health equity and increasing policy, systems and environmental changes. HEAL works: In schools:[[br]] HEAL encourages schools to adopt the Comprehensive School Physical Activity Program. This framework encourages students to be physically active for 60 minutes a day through school, home, and community activities. HEAL also tracks height and weight trends in elementary school students. In worksites:[[br]] HEAL offers training on developing worksite wellness programs called Work@Health. HEAL partners with local health departments to encourage worksites to complete the CDC Scorecard and participate in yearly health risk assessments for their employees. HEAL provides toolkits and other resources for employers interested in implementing wellness programs [https://heal.health.utah.gov/worksite-wellness/ Worksite Wellness]. In communities:[[br]] HEAL receives federal funding to partner with worksites and community-based organizations to increase access to fresh fruits and vegetables in worksite and community settings. HEAlL also partners with LHDs to work with cities and/or counties within their jurisdictions to create a built environment that encourages physical activity. In healthcare:[[br]] HEAL works with health care systems to establish community clinical linkages to support individuals at risk for or diagnosed with diabetes or hypertension to engage in lifestyle change programs such as chronic disease self-management and diabetes prevention programs. In childcare:[[br]] HEAL works with state and local partners through the Childcare Obesity Prevention workgroup to implement policy and systems changes in early care and education across agencies statewide. Ten local health departments statewide have implemented the TOP Star program, which aims to improve the nutrition, physical activity, and breastfeeding policies and environments and achieve best practices in childcare centers and homes.[[br]]Available Services
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services houses the Healthy Environments Active Living (HEAL) Program. The [https://heal.health.utah.gov/ HEAL website] has information on healthy living, including prevention of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.Health Program Information
Overarching Goals: Healthy People: Increase access to resources that empower all people in Utah to reach their full health potential. Healthy Communities: Increase the capacity of communities to support and promote healthy living for all individuals. Equitable Society: Increase opportunities for people who are under-resourced and under-represented in Utah to live healthy and thriving lives. Staff from the [https://heal.health.utah.gov/ HEAL] Program work with health care providers, including diabetes educators, dietitians, pharmacists, community health centers, community health workers, work-sites, and health plans to improve the care provided to Utahns with diabetes. Originally known as EPICC, (The Healthy Living through Environment, Policy, and Improved Clinical Care Program), the Healthy Environments Active Living (HEAL) Program is a program within the Utah Department of Health Bureau of Health Promotion. HEAL focuses on enabling education and engaged change for public health by engaging its three main audiences: individuals, partners, and decision makers. HEAL champions public health initiatives and addresses the challenges of making health awareness and access truly universal and equitable in eight key areas: nutrition, heart health, diabetes, physical activity, schools, child care, community health workers, and worksites.Related Indicators
Relevant Population Characteristics
There are considerable differences in the prevalence of obesity by subpopulations. For example, Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander adults and American Indian/Alaskan Native adults tend to have higher rates than the state rate.Related Relevant Population Characteristics Indicators:
Health Care System Factors
The cost of obesity is hard to specify, as the methods used can be very different for each study. One study, using data from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, found that medical costs for obese adults can be 42% higher than costs for adults at a normal weight for both public and private payers [Finkelstein EA, Trogdon JG, Cohen JW, Dietz W. Annual Medical Spending Attributable to Obesity: Payer-and Service-Specific Estimates. Health Affairs, 28(5): w822-831, 2009].Related Health Care System Factors Indicators:
Risk Factors
There are things that people can do that can reduce their risk of obesity. Behaviors such as engaging in physical activity and having a healthy diet can have a significant impact on reducing the risk (see [https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/causes.html/ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Overweight & Obesity: Adult Obesity Causes & Consequences.]).Related Risk Factors Indicators:
- Daily Fruit Consumption
- Daily Vegetable Consumption
- Arthritis Prevalence
- Blood Cholesterol: Doctor-diagnosed High Cholesterol
- Breast Cancer Incidence
- Colorectal Cancer Incidence
- Diabetes Prevalence
- Fair/poor health
- Blood Pressure: Doctor-diagnosed Hypertension
- Obesity Among Children and Adolescents
- Overweight or Obese
- Physical Activity: Recommended Aerobic Activity Among Adults
- Physical Activity: Recommended Muscle-strengthening Among Adults
- Prostate Cancer Incidence
Graphical Data Views
Obesity in the U.S. and in Utah continues to increase.
| BRFSS Utah vs. U.S. | Year | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 68 | ||||||
| UT Old Methodology | 1989 | 10.5% | 8.9% | 12.1% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1990 | 9.9% | 8.3% | 11.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1991 | 11.0% | 9.3% | 12.7% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1992 | 12.4% | 10.6% | 14.2% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1993 | 12.0% | 10.3% | 13.7% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1994 | 12.4% | 10.7% | 14.0% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1995 | 13.7% | 12.0% | 15.4% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1996 | 13.9% | 12.1% | 15.7% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1997 | 15.8% | 14.1% | 17.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1998 | 16.5% | 14.5% | 18.4% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1999 | 16.9% | 15.1% | 18.8% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2000 | 19.5% | 17.6% | 21.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2001 | 19.3% | 17.7% | 21.0% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2002 | 19.0% | 17.4% | 20.6% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2003 | 21.5% | 19.8% | 23.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2004 | 21.1% | 19.7% | 22.4% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2005 | 22.1% | 20.7% | 23.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2006 | 22.8% | 21.5% | 24.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2007 | 23.1% | 21.7% | 24.6% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2008 | 24.0% | 22.6% | 25.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2009 | 24.8% | 23.7% | 25.9% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2010 | 24.0% | 22.9% | 25.1% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1989 | 11.3% | 10.9% | 11.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1990 | 11.9% | 11.5% | 12.3% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1991 | 12.8% | 12.4% | 13.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1992 | 13.5% | 13.2% | 13.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1993 | 14.4% | 14.1% | 14.8% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1994 | 15.1% | 14.8% | 15.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1995 | 15.9% | 15.5% | 16.3% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1996 | 16.4% | 16.1% | 16.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1997 | 16.9% | 16.6% | 17.3% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1998 | 18.4% | 18.1% | 18.8% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1999 | 19.4% | 19.1% | 19.8% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2000 | 20.3% | 20.0% | 20.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2001 | 21.6% | 21.3% | 21.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2002 | 21.8% | 21.4% | 22.1% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2003 | 22.7% | 22.4% | 23.0% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2004 | 23.4% | 23.1% | 23.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2005 | 24.4% | 24.1% | 24.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2006 | 25.0% | 24.6% | 25.3% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2007 | 25.9% | 25.6% | 26.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2008 | 26.5% | 26.2% | 26.8% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2009 | 27.1% | 26.8% | 27.4% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2010 | 27.4% | 27.1% | 27.7% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2009 | 25.5% | 24.4% | 26.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2010 | 25.2% | 24.2% | 26.3% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2011 | 25.2% | 24.2% | 26.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2012 | 25.0% | 24.0% | 26.0% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2013 | 25.1% | 24.1% | 26.0% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2014 | 26.6% | 25.7% | 27.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2015 | 25.2% | 24.2% | 26.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2016 | 26.2% | 25.1% | 27.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2017 | 26.0% | 24.9% | 27.1% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2018 | 28.4% | 27.3% | 29.5% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2019 | 29.9% | 28.8% | 31.0% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2020 | 29.4% | 28.2% | 30.5% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2021 | 31.8% | 30.6% | 32.9% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2011 | 27.4% | 27.1% | 27.6% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2012 | 27.7% | 27.4% | 28.0% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2013 | 28.3% | 28.0% | 28.6% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2014 | 29.0% | 28.7% | 29.2% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2015 | 28.9% | 28.6% | 29.2% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2016 | 29.6% | 29.4% | 29.9% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2017 | 30.1% | 29.8% | 30.4% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2018 | 31.1% | 30.8% | 31.4% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2019 | 31.5% | 31.2% | 31.8% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2020 | 32.2% | 31.8% | 32.5% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2021 | 33.3% | 33.0% | 33.7% | ||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. [[br]]Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.[[br]] [[br]]U.S. data does not include U.S. territories, but does include Dist. of Columbia.[[br]] [[br]] Beginning in 2011, BRFSS data include both landline and cell phone respondent data along with a new weighting methodology called iterative proportional fitting, or raking. Comparisons between 2011 and prior years should be made with caution. More details about these changes can be found at: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/pdf/opha/resource/brfss/RakingImpact2011.pdf].Data Sources
- Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey Data, US Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)
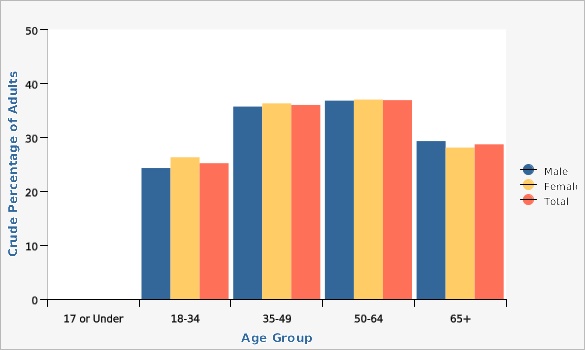
Rates shown are crude rates. The overall obesity rate for maies in 2021 was 30.5%, compared to 31.4% for females (not shown). Differences were not significantly different. The overall crude rate for obesity was 30.9% (29.8%-32.1%) in 2021 (not shown in the table).
| Males vs. Females | Age Group | Crude Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 13 | ||||||
| Male | 18-34 | 24.3% | 21.5% | 27.3% | ||
| Male | 35-49 | 35.7% | 32.6% | 38.9% | ||
| Male | 50-64 | 36.8% | 33.5% | 40.3% | ||
| Male | 65+ | 29.3% | 26.2% | 32.6% | ||
| Female | 17 or Under | ** | ||||
| Female | 18-34 | 26.3% | 23.1% | 29.9% | ||
| Female | 35-49 | 36.3% | 33.0% | 39.7% | ||
| Female | 50-64 | 37.0% | 33.5% | 40.7% | ||
| Female | 65+ | 28.1% | 25.2% | 31.3% | ||
| Total | 18-34 | 25.2% | 23.1% | 27.5% | ||
| Total | 35-49 | 36.0% | 33.7% | 38.3% | ||
| Total | 50-64 | 36.9% | 34.5% | 39.4% | ||
| Total | 65+ | 28.7% | 26.5% | 30.9% | ||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters.Data Source
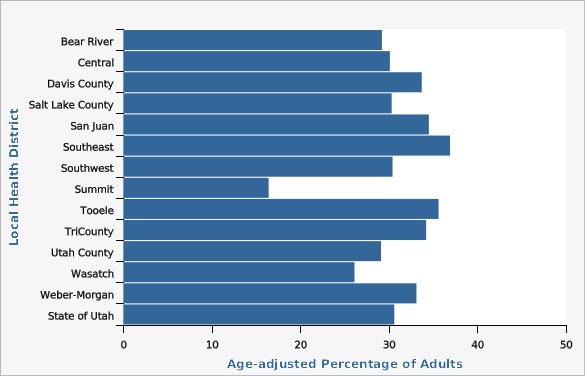
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)Southeast Utah had the highest obesity rate, folllowed closely by Tooele County.
| Local Health District | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 14 | ||||||
| Bear River | 29.2% | 26.2% | 32.5% | |||
| Central | 30.1% | 26.6% | 34.0% | |||
| Davis County | 33.7% | 31.0% | 36.4% | |||
| Salt Lake County | 30.3% | 28.9% | 31.8% | |||
| San Juan | 34.5% | 26.3% | 43.7% | |||
| Southeast | 36.9% | 31.5% | 42.6% | |||
| Southwest | 30.4% | 27.2% | 33.8% | |||
| Summit | 16.4% | 12.4% | 21.3% | |||
| Tooele | 35.6% | 31.2% | 40.3% | |||
| TriCounty | 34.2% | 30.7% | 37.8% | |||
| Utah County | 29.1% | 27.3% | 30.9% | |||
| Wasatch | 26.1% | 20.8% | 32.3% | |||
| Weber-Morgan | 33.1% | 30.3% | 36.1% | |||
| State of Utah | 30.6% | 29.8% | 31.4% | |||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. [[br]] [[br]] Percentages have been age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population. [[br]]Data Sources
- The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)
- Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey Data, US Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
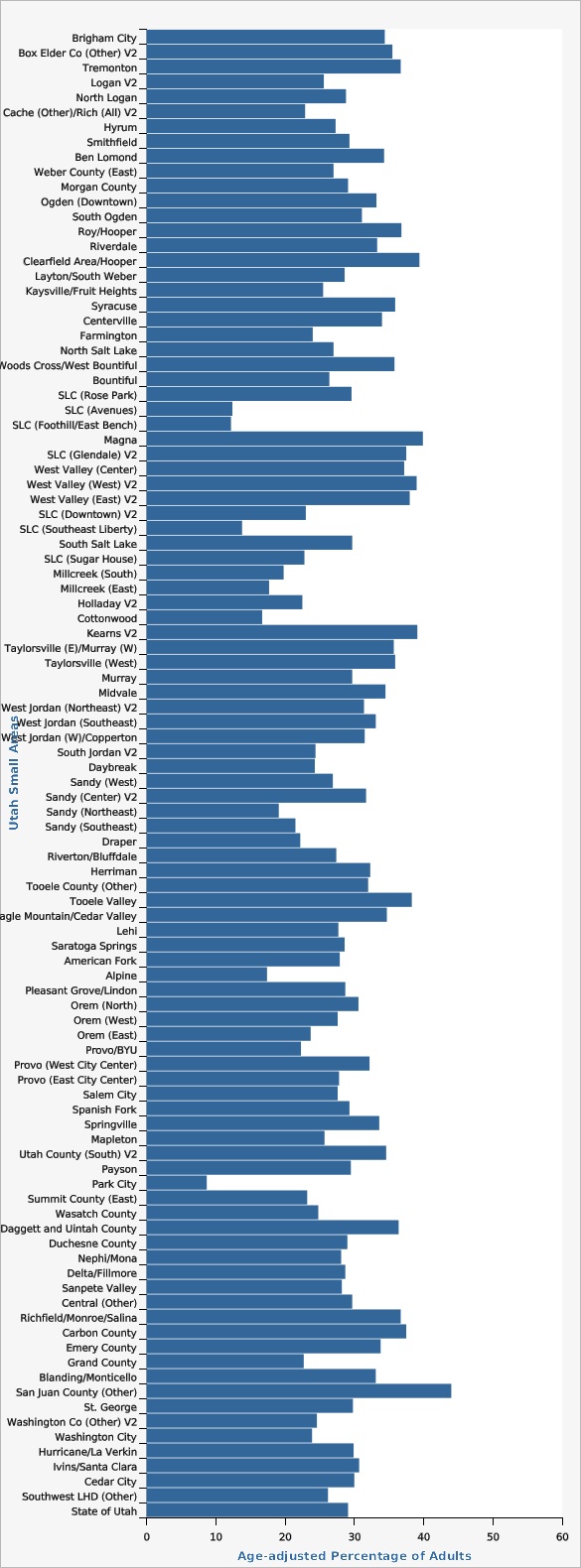
There was considerable variation in the rates of obesity by Utah Small Area. The gap between the areas with the lowest rate and the highest rate was dramatic. Park City had the lowest rate of obesity (8.7%) of all the Utah Small Areas. San Juan County (Other) had the highest rate of obesity (44.0%). Note that the state rate represents the rate for the combined five-year period.
| Utah Small Areas | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 100 | ||||||
| Brigham City | 34.4% | 29.1% | 40.1% | |||
| Box Elder Co (Other) V2 | 35.5% | 28.3% | 43.4% | |||
| Tremonton | 36.7% | 30.1% | 43.7% | |||
| Logan V2 | 25.6% | 22.2% | 29.4% | |||
| North Logan | 28.8% | 23.2% | 35.2% | |||
| Cache (Other)/Rich (All) V2 | 22.9% | 18.7% | 27.7% | |||
| Hyrum | 27.3% | 19.6% | 36.7% | |||
| Smithfield | 29.3% | 23.0% | 36.4% | |||
| Ben Lomond | 34.3% | 30.5% | 38.2% | |||
| Weber County (East) | 27.0% | 23.1% | 31.3% | |||
| Morgan County | 29.1% | 21.5% | 38.1% | |||
| Ogden (Downtown) | 33.2% | 28.7% | 38.0% | |||
| South Ogden | 31.1% | 26.5% | 36.0% | |||
| Roy/Hooper | 36.8% | 32.4% | 41.4% | |||
| Riverdale | 33.3% | 28.0% | 39.1% | |||
| Clearfield Area/Hooper | 39.4% | 35.4% | 43.5% | |||
| Layton/South Weber | 28.6% | 25.6% | 31.8% | |||
| Kaysville/Fruit Heights | 25.5% | 21.3% | 30.2% | |||
| Syracuse | 35.9% | 30.5% | 41.6% | |||
| Centerville | 34.0% | 26.7% | 42.1% | |||
| Farmington | 24.0% | 18.6% | 30.4% | |||
| North Salt Lake | 27.0% | 20.8% | 34.3% | |||
| Woods Cross/West Bountiful | 35.8% | 28.0% | 44.4% | |||
| Bountiful | 26.4% | 22.4% | 30.9% | |||
| SLC (Rose Park) | 29.6% | 24.5% | 35.3% | |||
| SLC (Avenues) | 12.4% | 8.8% | 17.3% | |||
| SLC (Foothill/East Bench) | 12.2% | 8.7% | 17.0% | |||
| Magna | 39.9% | 34.3% | 45.8% | |||
| SLC (Glendale) V2 | 37.5% | 30.4% | 45.1% | |||
| West Valley (Center) | 37.2% | 32.4% | 42.2% | |||
| West Valley (West) V2 | 39.0% | 32.9% | 45.6% | |||
| West Valley (East) V2 | 38.0% | 33.3% | 42.9% | |||
| SLC (Downtown) V2 | 23.0% | 18.8% | 28.0% | |||
| SLC (Southeast Liberty) | 13.8% | 9.7% | 19.3% | |||
| South Salt Lake | 29.7% | 24.1% | 35.8% | |||
| SLC (Sugar House) | 22.8% | 18.9% | 27.2% | |||
| Millcreek (South) | 19.8% | 15.2% | 25.5% | |||
| Millcreek (East) | 17.7% | 13.2% | 23.4% | |||
| Holladay V2 | 22.5% | 16.9% | 29.2% | |||
| Cottonwood | 16.7% | 13.2% | 20.9% | |||
| Kearns V2 | 39.1% | 33.7% | 44.7% | |||
| Taylorsville (E)/Murray (W) | 35.7% | 31.0% | 40.7% | |||
| Taylorsville (West) | 35.9% | 30.8% | 41.4% | |||
| Murray | 29.7% | 24.8% | 35.1% | |||
| Midvale | 34.5% | 29.2% | 40.2% | |||
| West Jordan (Northeast) V2 | 31.4% | 26.6% | 36.8% | |||
| West Jordan (Southeast) | 33.1% | 28.6% | 38.1% | |||
| West Jordan (W)/Copperton | 31.5% | 26.8% | 36.6% | |||
| South Jordan V2 | 24.4% | 20.4% | 28.9% | |||
| Daybreak | 24.3% | 19.5% | 29.8% | |||
| Sandy (West) | 26.9% | 21.8% | 32.6% | |||
| Sandy (Center) V2 | 31.7% | 26.3% | 37.6% | |||
| Sandy (Northeast) | 19.1% | 14.5% | 24.7% | |||
| Sandy (Southeast) | 21.5% | 16.9% | 27.0% | |||
| Draper | 22.2% | 17.9% | 27.2% | |||
| Riverton/Bluffdale | 27.4% | 23.5% | 31.7% | |||
| Herriman | 32.3% | 27.8% | 37.1% | |||
| Tooele County (Other) | 32.0% | 26.7% | 37.8% | |||
| Tooele Valley | 38.3% | 35.1% | 41.6% | |||
| Eagle Mountain/Cedar Valley | 34.7% | 29.1% | 40.8% | |||
| Lehi | 27.7% | 24.3% | 31.3% | |||
| Saratoga Springs | 28.6% | 23.4% | 34.4% | |||
| American Fork | 27.9% | 24.0% | 32.1% | |||
| Alpine | 17.4% | 11.4% | 25.5% | |||
| Pleasant Grove/Lindon | 28.7% | 25.2% | 32.5% | |||
| Orem (North) | 30.6% | 26.1% | 35.5% | |||
| Orem (West) | 27.6% | 23.4% | 32.2% | |||
| Orem (East) | 23.7% | 18.9% | 29.3% | |||
| Provo/BYU | 22.3% | 18.4% | 26.8% | |||
| Provo (West City Center) | 32.2% | 27.3% | 37.6% | |||
| Provo (East City Center) | 27.8% | 21.3% | 35.5% | |||
| Salem City | 27.6% | 20.5% | 36.1% | |||
| Spanish Fork | 29.3% | 25.4% | 33.6% | |||
| Springville | 33.6% | 28.9% | 38.7% | |||
| Mapleton | 25.7% | 19.5% | 33.0% | |||
| Utah County (South) V2 | 34.6% | 28.0% | 41.9% | |||
| Payson | 29.5% | 24.6% | 34.9% | |||
| Park City | 8.7% | 6.0% | 12.5% | |||
| Summit County (East) | 23.2% | 18.4% | 28.8% | |||
| Wasatch County | 24.8% | 21.4% | 28.6% | |||
| Daggett and Uintah County | 36.4% | 33.6% | 39.3% | |||
| Duchesne County | 29.0% | 25.8% | 32.5% | |||
| Nephi/Mona | 28.1% | 21.6% | 35.7% | |||
| Delta/Fillmore | 28.7% | 23.2% | 35.0% | |||
| Sanpete Valley | 28.2% | 23.8% | 33.0% | |||
| Central (Other) | 29.7% | 25.7% | 34.0% | |||
| Richfield/Monroe/Salina | 36.7% | 31.5% | 42.1% | |||
| Carbon County | 37.5% | 33.0% | 42.2% | |||
| Emery County | 33.8% | 28.4% | 39.7% | |||
| Grand County | 22.7% | 16.9% | 29.6% | |||
| Blanding/Monticello | 33.1% | 27.6% | 39.0% | |||
| San Juan County (Other) | 44.0% | 34.8% | 53.6% | |||
| St. George | 29.8% | 26.6% | 33.2% | |||
| Washington Co (Other) V2 | 24.6% | 17.7% | 33.1% | |||
| Washington City | 23.9% | 18.6% | 30.3% | |||
| Hurricane/La Verkin | 29.9% | 23.9% | 36.7% | |||
| Ivins/Santa Clara | 30.7% | 22.2% | 40.6% | |||
| Cedar City | 30.0% | 25.6% | 34.8% | |||
| Southwest LHD (Other) | 26.2% | 21.1% | 32.1% | |||
| State of Utah | 29.1% | 28.6% | 29.6% | |||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. [[br]] [[br]] Percentages have been age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population. [[br]] [[br]]A description of the Utah Small Areas and details about Small Area reclassification may be found on the Methodology and Guidelines page at: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/resource/Guidelines.html].Data Source
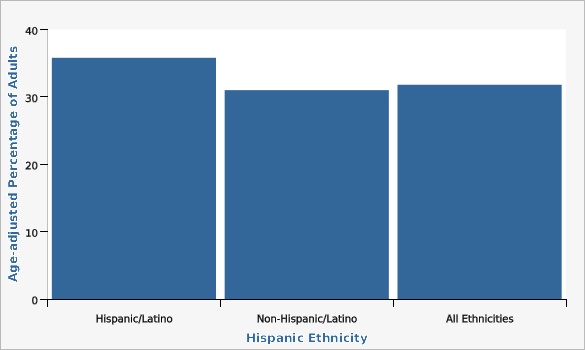
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)Adults who are Hispanic or Latino have statistically significantly higher rates of obesity than adults who are non-Hispanic.
| Hispanic Ethnicity | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Hispanic/Latino | 35.8% | 32.1% | 39.8% | |||
| Non-Hispanic/Latino | 31.0% | 29.7% | 32.2% | |||
| All Ethnicities | 31.8% | 30.6% | 32.9% | |||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. [[br]] [[br]] Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
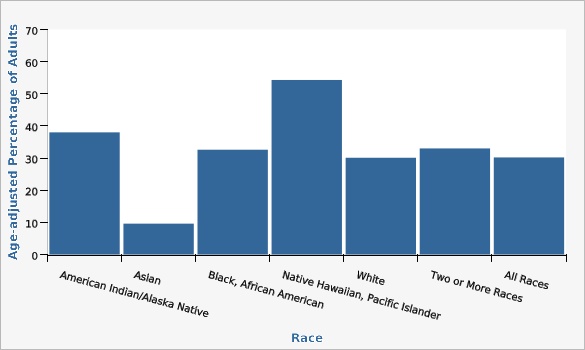
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)The highest rate of obesity was seen for Pacific Islander adults (54.3%) lowest rate was reported for Asian adults (9.6%).
| Race | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 7 | ||||||
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 38.0% | 32.6% | 43.7% | |||
| Asian | 9.6% | 6.8% | 13.3% | |||
| Black, African American | 32.6% | 26.3% | 39.6% | |||
| Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islander | 54.3% | 45.1% | 63.2% | |||
| White | 30.1% | 29.4% | 30.8% | |||
| Two or More Races | 33.0% | 30.0% | 36.2% | |||
| All Races | 30.2% | 29.6% | 30.9% | |||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. [[br]] [[br]] Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population with three age groups.[[br]] [[br]]Three years of data were combined to improve reliability of the estimates.Data Source
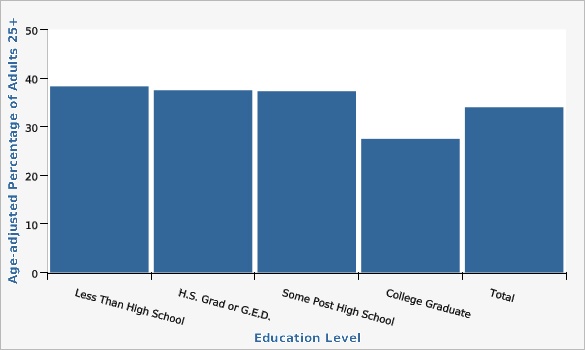
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)Data were limited to adults aged 25 or older. Adults with a college degree or higher had the lowest rate of obesity of any of the education groups.
| Education Level | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults 25+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| Less Than High School | 38.3% | 32.2% | 44.8% | |||
| H.S. Grad or G.E.D. | 37.5% | 34.7% | 40.3% | |||
| Some Post High School | 37.3% | 35.0% | 39.6% | |||
| College Graduate | 27.5% | 25.8% | 29.2% | |||
| Total | 34.0% | 32.7% | 35.3% | |||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. [[br]] [[br]] Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
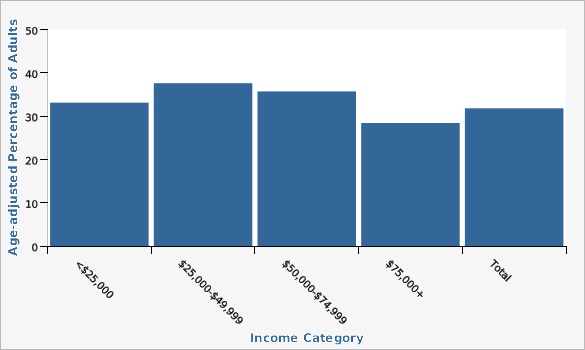
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)Lower rates of obesity are seen for adults in households with annal incomes of $75,000 or higher.
| Income Category | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| <$25,000 | 33.1% | 28.9% | 37.6% | |||
| $25,000-$49,999 | 37.6% | 34.7% | 40.6% | |||
| $50,000-$74,999 | 35.7% | 32.7% | 38.9% | |||
| $75,000+ | 28.4% | 26.7% | 30.2% | |||
| Total | 31.8% | 30.6% | 32.9% | |||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. [[br]] [[br]] Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
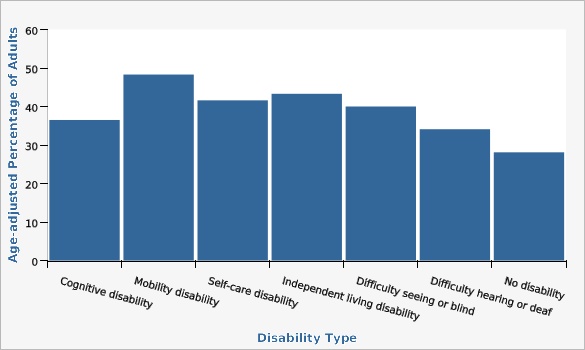
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)Disability can make it more challenging to be active, eat well, and control weight (see [https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/obesity.html]). The highest rates of obesity is seen for adults with mobility disabilities.
| Disability Type | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 7 | ||||||
| Cognitive disability | 36.5% | 34.0% | 39.2% | |||
| Mobility disability | 48.3% | 44.2% | 52.4% | |||
| Self-care disability | 41.6% | 34.8% | 48.8% | |||
| Independent living disability | 43.3% | 39.5% | 47.2% | |||
| Difficulty seeing or blind | 40.0% | 34.3% | 46.0% | |||
| Difficulty hearing or deaf | 34.1% | 29.4% | 39.1% | |||
| No disability | 28.1% | 27.2% | 29.0% | |||
Data Notes
Obesity is defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. BMI is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of height in meters. Rates are age-adjusted.Two years of data were combined to increase reliability of the estimates.Data Source
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS)References and Community Resources
The National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion provides consumer information at [https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/index.html]. NHLBI Obesity Education Initiative - [https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/science/obesity-nutrition-and-physical-activity] Trust for America's Health - [https://www.tfah.org/]More Resources and Links
Evidence-based community health improvement ideas and interventions may be found at the following sites:- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) WONDER Database, a system for disseminating public health data and information.
- United States Census Bureau data dashboard.
- Utah healthy Places Index, evidence-based and peer-reviewed tool, supports efforts to prioritize equitable community investments, develop critical programs and policies across the state, and much more.
- County Health Rankings
- Kaiser Family Foundation's StateHealthFacts.org
- Medical literature can be queried at PubMed library.
Page Content Updated On 10/31/2022,
Published on 12/20/2022