Complete Health Indicator Report of Prostate Cancer Screening
Definition
The percentage of men aged 40 and above who reported having a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test in the last five years or who reported ever having had a PSA test.Numerator
The number of men aged 40 and above who reported having had a PSA test within the specified time period.Denominator
The total number of male survey respondents aged 40 or older excluding those who responded "don't know" or "refused" to the numerator question.Data Interpretation Issues
To reduce bias and more accurately represent population data, the BRFSS has changed survey methodology. In 2010, it began conducting surveys by cellular phone in addition to landline phones. It also adopted "iterative proportional fitting" (raking) as its weighting method. More details about these changes can be found at: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/pdf/opha/resource/brfss/RakingImpact2011.pdf].Why Is This Important?
Prostate cancer is the most commonly occurring form of cancer (excluding skin cancer) among men and is the second leading cause of cancer death for men in Utah and the U.S. All men over 40 should visit their doctor for a routine health visit which may include a discussion on prostate health.How Are We Doing?
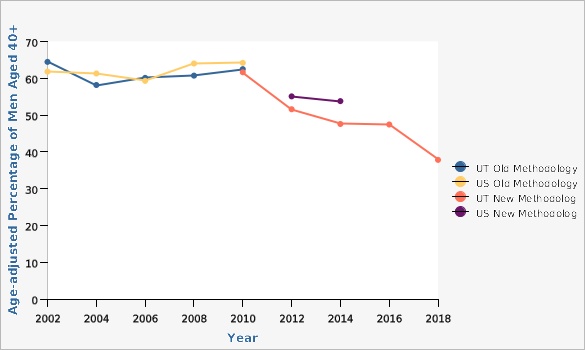
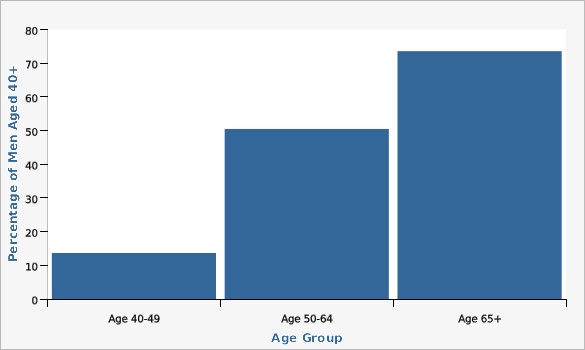
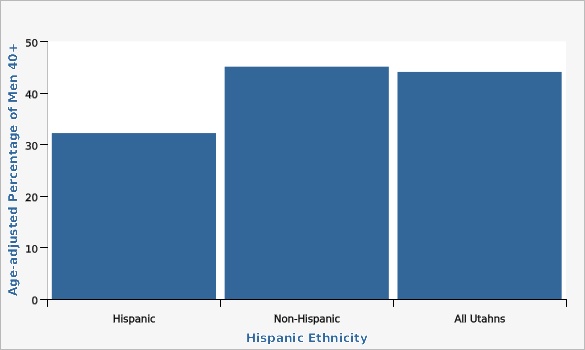
In 2018, 37.8 percent of Utah men aged 40 and older reported ever receiving a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test (age-adjusted rate). Since 2010, PSA testing has been declining which is expected since routine testing is no longer recommended (see Evidence-based Practices section). PSA testing rates in Utah increased significantly with age. For example, 13.7 percent of men aged 40 to 49 had ever had a PSA compared with 50.5 percent of men aged 50 to 64 (2014-2018 data). From 2014-2018 Hispanic men were less likely then non-Hispanic men to report ever having had a PSA test (32.2 percent compared with 45.1 percent).How Do We Compare With the U.S.?
Historically, since 2002 rates of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the Utah male population have shown little difference in comparison to U.S. rates. However, in 2012 and 2014, Utah males aged 40 and older were less likely to have ever had a PSA test than U.S. males of the same age (47.6 percent of Utah males compared with 53.8 percent of U.S. males in 2014).Evidence-based Practices
Screening recommendations have changed over time. Until recently, many doctors and professional organizations encouraged yearly prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening for men beginning at age 50. However, as more has been learned about both the benefits and harms of prostate cancer screening, a number of organizations have begun to caution against routine population screening. Although some organizations continue to recommend PSA screening, there is widespread agreement that any man who is considering getting tested should first be informed in detail about the potential harms and benefits. Currently, Medicare provides coverage for an annual PSA test for all Medicare-eligible men age 50 and older. Many private insurers cover PSA screening as well. Since 2012, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends against PSA-based screening for prostate cancer. Healthy diet, exercise, and lifestyle play an important role in cancer prevention.Related Indicators
Related Relevant Population Characteristics Indicators:
Graphical Data Views
| BRFSS Utah vs. U.S. | Year | Age-adjusted Percentage of Men Aged 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 17 | ||||||
| UT Old Methodology | 2002 | 64.4% | 61.0% | 67.8% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2004 | 58.2% | 55.3% | 61.0% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2006 | 60.1% | 57.5% | 62.7% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2008 | 60.7% | 58.0% | 63.4% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2010 | 62.5% | 60.6% | 64.4% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2002 | 61.8% | 61.1% | 62.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2004 | 61.3% | 60.7% | 61.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2006 | 59.3% | 58.7% | 59.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2008 | 64.0% | 63.5% | 64.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2010 | 64.2% | 63.7% | 64.7% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2010 | 61.6% | 59.7% | 63.5% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2012 | 51.6% | 49.7% | 53.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2014 | 47.6% | 46.0% | 49.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2016 | 47.4% | 45.4% | 49.5% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2018 | 37.8% | 36.0% | 39.6% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2012 | 55.1% | 54.5% | 55.7% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2014 | 53.8% | 53.2% | 54.4% | ||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population. Old Methodology: Previous BRFSS methodology used "post-stratification" which was used to weight data by age, gender, and local health district (LHD). New Methodology: To reduce bias and more accurately represent population data, the BRFSS has changed survey methodology. It began conducting surveys by cellular phone in addition to landline phones. It also adopted "iterative proportional fitting" (raking) as its weighting method. With raking, education, race/ethnicity, marital status, home ownership/renter, and telephone source are included in the weighting procedure. Due to changes in sampling and weighting methodology, data from the new methodology represents a new baseline, and comparisons from new to old methodology data are not appropriate.Data Sources
- Utah Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Office of Public Health Assessment, Utah Department of Health
- U.S. Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), Division of Behavioral Surveillance, CDC Office of Surveillance, Epidemiology, and Laboratory Services
| Local Health District | Age-adjusted Percentage of Men 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 14 | ||||||
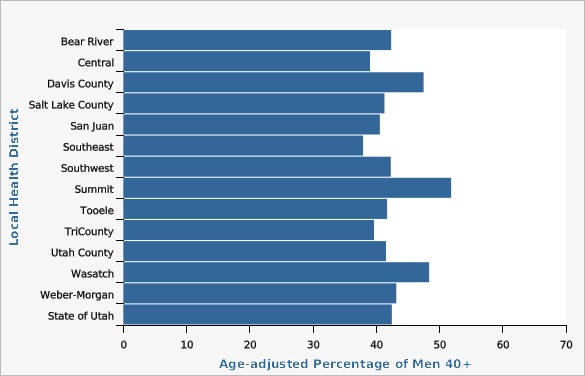
| Bear River | 42.3% | 37.7% | 47.1% | |||
| Central | 39.0% | 34.3% | 43.9% | |||
| Davis County | 47.5% | 43.2% | 51.8% | |||
| Salt Lake County | 41.3% | 38.8% | 43.8% | |||
| San Juan | 40.6% | 31.7% | 50.0% | |||
| Southeast | 37.9% | 31.2% | 45.1% | |||
| Southwest | 42.3% | 37.7% | 47.0% | |||
| Summit | 51.8% | 43.0% | 60.6% | |||
| Tooele | 41.7% | 34.7% | 49.0% | |||
| TriCounty | 39.6% | 34.4% | 45.2% | |||
| Utah County | 41.5% | 38.3% | 44.8% | |||
| Wasatch | 48.4% | 41.6% | 55.1% | |||
| Weber-Morgan | 43.2% | 38.9% | 47.5% | |||
| State of Utah | 42.4% | 41.1% | 43.8% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population. Prior to 2015 San Juan County was part of the Southeast Local Health District. In 2015 the San Juan County Local Health District was formed. Data reported are for all years using the current boundaries.Data Source
Utah Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Office of Public Health Assessment, Utah Department of Health| Age Group | Percentage of Men Aged 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Age 40-49 | 13.7% | 12.2% | 15.4% | |||
| Age 50-64 | 50.5% | 48.5% | 52.5% | |||
| Age 65+ | 73.6% | 71.7% | 75.4% | |||
Data Source
Utah Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Office of Public Health Assessment, Utah Department of Health| Hispanic Ethnicity | Age-adjusted Percentage of Men 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Hispanic | 32.2% | 27.5% | 37.3% | |||
| Non-Hispanic | 45.1% | 44.0% | 46.2% | |||
| All Utahns | 44.1% | 43.0% | 45.2% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
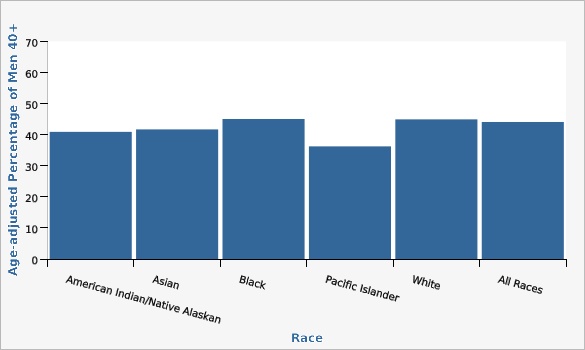
Utah Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Office of Public Health Assessment, Utah Department of Health| Race | Age-adjusted Percentage of Men 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 6 | ||||||
| American Indian/Native Alaskan | 40.9% | 31.8% | 50.7% | |||
| Asian | 41.7% | 33.8% | 50.1% | |||
| Black | 45.1% | 32.9% | 57.8% | |||
| Pacific Islander | 36.2% | 16.1% | 62.7% | * | ||
| White | 44.9% | 43.9% | 46.0% | |||
| All Races | 44.1% | 43.0% | 45.2% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population. [[br]] *Use caution in interpreting, the estimate has a relative standard error greater than 30% and does not meet UDOH standards for reliability. For more information, please go to [http://ibis.health.utah.gov/pdf/resource/DataSuppression.pdf].[[br]]Data Source
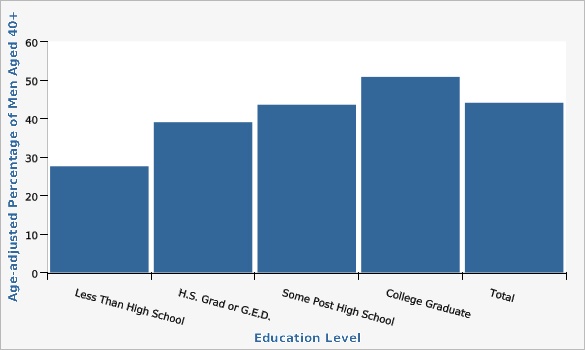
Utah Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Office of Public Health Assessment, Utah Department of Health| Education Level | Age-adjusted Percentage of Men Aged 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| Less Than High School | 27.6% | 23.0% | 32.8% | |||
| H.S. Grad or G.E.D. | 39.0% | 36.9% | 41.2% | |||
| Some Post High School | 43.6% | 41.6% | 45.5% | |||
| College Graduate | 50.8% | 49.4% | 52.3% | |||
| Total | 44.1% | 43.0% | 45.2% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
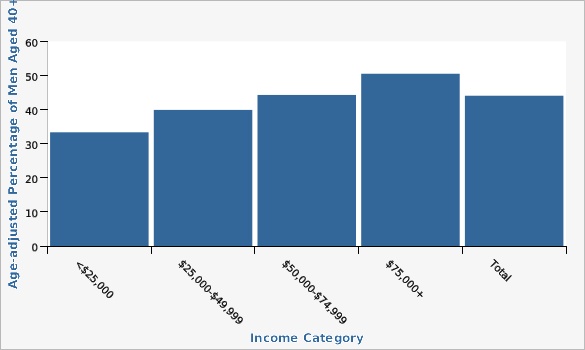
Utah Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Office of Public Health Assessment, Utah Department of Health| Income Category | Age-adjusted Percentage of Men Aged 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| <$25,000 | 33.4% | 30.2% | 36.6% | |||
| $25,000-$49,999 | 39.9% | 37.2% | 42.7% | |||
| $50,000-$74,999 | 44.3% | 42.0% | 46.7% | |||
| $75,000+ | 50.5% | 49.0% | 52.1% | |||
| Total | 44.1% | 43.0% | 45.2% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
Utah Data: Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, Office of Public Health Assessment, Utah Department of HealthReferences and Community Resources
Cancer Society: [http://www.cancer.org][[br]] National Cancer Institute: [http://www.cancer.gov][[br]] Huntsman Cancer Institute: [http://www.huntsmancancer.org][[br]] Utah Cancer Control Program: [http://www.cancerutah.org][[br]] Utah Cancer Action Network: [http://www.ucan.cc]More Resources and Links
Evidence-based community health improvement ideas and interventions may be found at the following sites:- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) WONDER Database, a system for disseminating public health data and information.
- United States Census Bureau data dashboard.
- Utah healthy Places Index, evidence-based and peer-reviewed tool, supports efforts to prioritize equitable community investments, develop critical programs and policies across the state, and much more.
- County Health Rankings
- Kaiser Family Foundation's StateHealthFacts.org
- Medical literature can be queried at PubMed library.
Page Content Updated On 10/08/2020,
Published on 03/12/2021