Complete Health Indicator Report of Parkinson's Disease
Definition
Utah residents who have been diagnosed with Parkinson's DiseaseNumerator
__Parkinson's Hospitalizations__: Number of hospitalizations among Utah Residents due to Parkinson's Disease (ICD9 code 332; ICD10 codes G20-G21) __Parkinson's Mortality__: Number of deaths among Utah residents due to Parkinson's Disease (ICD10 codes G20-G21) __Parkinson's Registry__: Number of Utah Residents with the characteristic of interestDenominator
Total number of persons in the population of Utah.Data Interpretation Issues
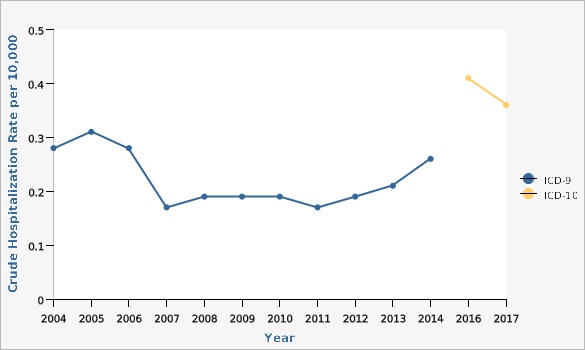
Beginning in 2016, coding for hospitalizations changed from ICD 9 to ICD 10. The impact of this coding change is unknown at this time. Interpretations of Parkinson's Disease hospitalizations over this time change should be made with caution.Why Is This Important?
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a progressive neurological brain disorder that affects movement. It is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer's disease. PD belongs to a group of conditions called motor system disorders, which are the result of a loss of dopamine-producing brain cells. The four primary symptoms of PD are tremor, rigidity/stiffness, bradykinesia (slowness of movement) and postural instability. Early symptoms of PD are subtle and occur gradually. As symptoms become more severe, carrying out activities of daily life can become difficult. PD usually affects people over the age of 60; however, younger onset of the disease can occur. Other symptoms may include depression, anxiety; difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking; urinary problems or constipation; skin problems; and sleep disruptions. There are currently no blood or laboratory tests used to diagnose PDl Diagnosis is based on medical history and a neurological examination. The disease can be difficult to diagnose accurately. Doctors may sometimes request brain scans or laboratory tests in order to rule out other diseases (National Institutes of Health). The combined direct and indirect cost of Parkinson's, including treatment, social security payments and lost income, is estimated to be nearly $25 billion per year in the United States alone. Medications alone cost an average of $2,500 a year and therapeutic surgery can cost up to $100,000 per person (Parkinson's Foundation).How Are We Doing?
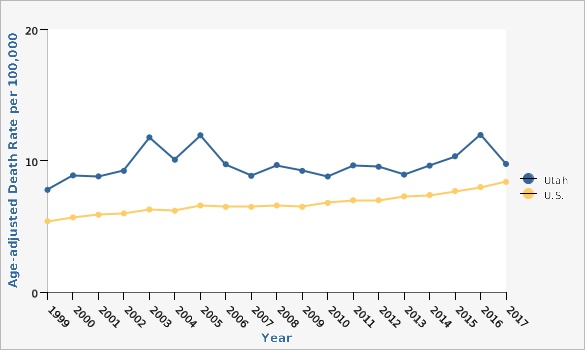
Approximately 5,000 Utahns have PD (Parkinson's Foundation). The Utah Parkinson's Disease registry contained 2,412 residents living with Parkinson's Disease as of December 2018. In 2017 the age-adjusted death rate in Utah was 9.8 per 100,000 people (IBIS).How Do We Compare With the U.S.?
About one million Americans live with Parkinson's disease (PD). Approximately 60,000 Americans are diagnosed with PD each year. Incidence of Parkinson's disease increases with age, but an estimated four percent of people with PD are diagnosed before age 50 (Parkinson's Foundation). The 2017 age-adjusted death rate for the United States was 8.4 per 100,000 people (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), lower than the Utah rate.What Is Being Done?
Utah has established the Utah Parkinson's Disease Registry to improve knowledge about the causes and treatment of PD. Collecting and analyzing this information in an entire state will provide important clues about potential causes of the disease, as well as help to ensure that adequate health care resources are available for all patients. A Parkinson's Disease Registry State Advisory Committee -- a collaboration of the Utah Department of Health, University of Utah Department of Neurology, Intermountain Neurosciences, individuals with PD, and other health care providers -- has been established to develop a state plan to guide the development of the registry. Resources for patients and their families are available through: (1) University of Utah Department of Neurology, sponsor of the Mountain West Parkinson's Initiative (MWPI) which serves the Mountain West region, and (2) Intermountain Neurosciences Institute.Evidence-based Practices
There is no cure for PD but drug therapy and surgery options can alleviate PD symptoms. Regular aerobic exercise slows the progression of PD. Levodopa is the most effective treatment for PD; it is used to treat motor symptoms. This medication is taken orally and travels to the brain. When it crosses the blood-brain barrier, it is converted to dopamine. There are a variety of other medications that are used to treat motor systems related to PD based of the effectiveness for the individual (Connolly & Lang). Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is the most commonly performed surgical treatment for PD. In DBS surgery, thin wires called electrodes are placed into one or both sides of the brain in specific areas that control movement. DBS typically works best to lessen motor symptoms like stiffness, slowness and tremor (Michael J. Fox Parkinson's Foundation). In addition to medications and surgical options, other important interventions can benefit individuals with PD. PD patients will have better outcomes if treated by a neurologist. A neurologist specializes in disorders of the central nervous system (Willis, et al.). Regular aerobic-type exercise leading to overall fitness has compelling evidence for slowing of PD progression. There are many programs available such as Rock Steady Boxing (Combs, et al.), Dance for PD (Dance for PD), and LSVT Big and Loud Therapy (Salgado, et al.). All patients with PD should be encouraged to engage in regular exercise (Ahlskog).Available Services
Mountain West Parkinson Initiative[[br]] [http://www.mwparkinson.org/] Mountain West Parkinson's Initiative at the Brain Health Learning[[br]] 729 Arapeen Drive, SLC, UT 84108[[br]] 801-585-2354 Intermountain Neurosciences Institute[[br]] 5171 S Cottonwood St 810[[br]] Murray, UT 84107[[br]] 801-507-9800 For questions contact:[[br]] Parkinson's Disease Registry[[br]] 801-585-2354Health Program Information
The Utah Chapter of the American Parkinson's Disease Association holds an annual symposium every fall. All people with the condition and caregivers are invited to attend the symposium to hear about the latest medical care from expert speakers. The Utah Chapter has also established support groups throughout the state.Related Indicators
Relevant Population Characteristics
About one million people in North American have Parkinson's disease. Approximately 13 out of 100,000 people have been diagnosed. Source: Statistics about Parkinson's | Parkinson's Foundation | [http://www.parkinson.org parkinson.org][[br]] [http://www.parkinson.org/statistics]Related Relevant Population Characteristics Indicators:
Health Care System Factors
The combined direct and indirect cost of Parkinson's in the U.S. is estimated to be nearly $25 billion each year. Much of this cost is for medications, which cost as average of $2,500 per year. Therapeutic surgery is another large expense and can cost up to $100,000 per person. Source: [http://www.parkinson.org/Understanding-Parkinsons/Causes-and-Statistics/Statistics]Risk Factors
The greatest risk factor for Parkinson's Disease (PD) is age. About 1-2% of adults over the age of 65 and about 0.3% of the general population have PD. PD occurs infrequently in the population under 40 years of age and early onset has been associated with the probability of genetic causes. The role of sex as a risk factor of PD is disputed. Some studies have found women to be at higher risk for PD, while others have found men to be at higher risk, and others have found no difference. Differences between men and women may also vary by ethnicity. Studies have found associations of smoking and caffeine consumption with decreased rates of PD and head injury and pesticide exposure with increased rates.Health Status Outcomes
Not all people with Parkinson's have the same symptoms. The most noticeable symptoms of Parkinson's are tremors, slow movements, balance problems, and rigidity. Some people experience cognitive impairment, mood disorders which can include anxiety and depression.They may also have sleep difficulties, speech or swallowing problems. Source: [https://www.michaeljfox.org/understanding-parkinsons/i-have-got-what.php?navid=diagnosis&smcid=ag-a30U0000000OXAo&s_src=Adwords&s_subsrc=what_is_parkinsons&gclid=EAIaIQobChMIj4X2-4KQ2gIVFIZ-Ch18mA0tEAAYAiAAEgLxo_D_BwE]Graphical Data Views
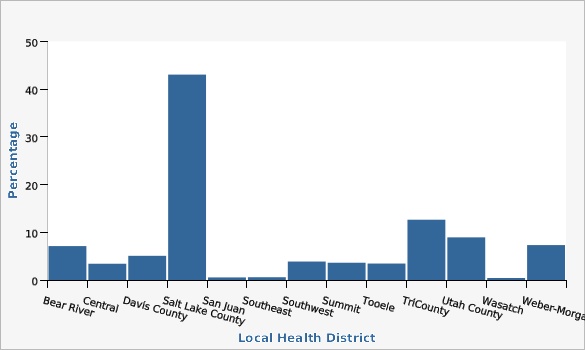
Parkinson's Disease Registry Distribution by Local Health District, Utah, December 2018
| Local Health District | Percentage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 13 | ||||||
| Bear River | 7.1% | |||||
| Central | 3.4% | |||||
| Davis County | 5.1% | |||||
| Salt Lake County | 43.1% | |||||
| San Juan | 0.5% | |||||
| Southeast | 0.6% | |||||
| Southwest | 3.9% | |||||
| Summit | 3.6% | |||||
| Tooele | 3.4% | |||||
| TriCounty | 12.6% | |||||
| Utah County | 8.9% | |||||
| Wasatch | 0.4% | |||||
| Weber-Morgan | 7.3% | |||||
Data Notes
Registry includes patients who have died. Participation in the registry is voluntary and not necessarily representative of the distribution of patients throughout the State.Data Source
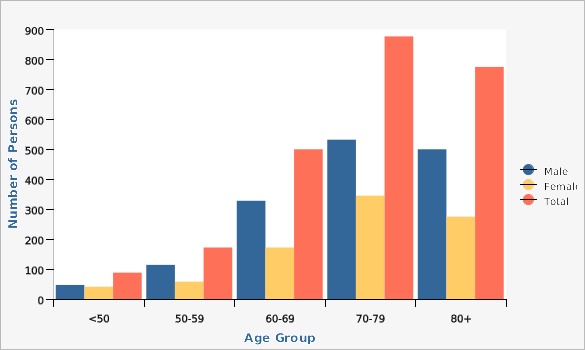
Utah Parkinson Disease Registry, Mountain West Parkinson Initiative, University of Utah Department of Neurology, Imaging and NeurosciencesParkinson's Disease Registry Distribution by Age and Sex, Utah, December 2018
| Males vs. Females | Age Group | Number of Persons | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 15 | ||||||
| Male | <50 | 47 | ||||
| Male | 50-59 | 114 | ||||
| Male | 60-69 | 328 | ||||
| Male | 70-79 | 532 | ||||
| Male | 80+ | 500 | ||||
| Female | <50 | 41 | ||||
| Female | 50-59 | 58 | ||||
| Female | 60-69 | 172 | ||||
| Female | 70-79 | 345 | ||||
| Female | 80+ | 275 | ||||
| Total | <50 | 88 | ||||
| Total | 50-59 | 172 | ||||
| Total | 60-69 | 500 | ||||
| Total | 70-79 | 877 | ||||
| Total | 80+ | 775 | ||||
Data Notes
Registry includes patients who have died. Participation in the registry is voluntary and not necessarily representative of the distribution of patients throughout the State.Data Source
Utah Parkinson Disease Registry, Mountain West Parkinson Initiative, University of Utah Department of Neurology, Imaging and Neurosciences| Utah vs. U.S. | Year | Age-adjusted Death Rate per 100,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 38 | ||||||
| Utah | 1999 | 7.8 | 6.4 | 9.4 | ||
| Utah | 2000 | 8.9 | 7.4 | 10.6 | ||
| Utah | 2001 | 8.8 | 7.4 | 10.4 | ||
| Utah | 2002 | 9.2 | 7.8 | 10.9 | ||
| Utah | 2003 | 11.8 | 10.2 | 13.6 | ||
| Utah | 2004 | 10.1 | 8.6 | 11.8 | ||
| Utah | 2005 | 12.0 | 10.4 | 13.7 | ||
| Utah | 2006 | 9.7 | 8.3 | 11.3 | ||
| Utah | 2007 | 8.9 | 7.5 | 10.4 | ||
| Utah | 2008 | 9.7 | 8.3 | 11.2 | ||
| Utah | 2009 | 9.2 | 7.9 | 10.7 | ||
| Utah | 2010 | 8.8 | 7.5 | 10.2 | ||
| Utah | 2011 | 9.7 | 8.3 | 11.1 | ||
| Utah | 2012 | 9.6 | 8.2 | 11.0 | ||
| Utah | 2013 | 9.0 | 7.7 | 10.3 | ||
| Utah | 2014 | 9.6 | 8.4 | 11.0 | ||
| Utah | 2015 | 10.4 | 9.0 | 11.8 | ||
| Utah | 2016 | 12.0 | 10.6 | 13.5 | ||
| Utah | 2017 | 9.8 | 8.5 | 11.1 | ||
| U.S. | 1999 | 5.4 | 5.3 | 5.5 | ||
| U.S. | 2000 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 5.8 | ||
| U.S. | 2001 | 5.9 | 5.8 | 6.0 | ||
| U.S. | 2002 | 6.0 | 5.9 | 6.1 | ||
| U.S. | 2003 | 6.3 | 6.2 | 6.4 | ||
| U.S. | 2004 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 6.3 | ||
| U.S. | 2005 | 6.6 | 6.5 | 6.7 | ||
| U.S. | 2006 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 6.6 | ||
| U.S. | 2007 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 6.6 | ||
| U.S. | 2008 | 6.6 | 6.5 | 6.7 | ||
| U.S. | 2009 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 6.6 | ||
| U.S. | 2010 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 6.9 | ||
| U.S. | 2011 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 7.1 | ||
| U.S. | 2012 | 7.0 | 6.9 | 7.1 | ||
| U.S. | 2013 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.4 | ||
| U.S. | 2014 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.5 | ||
| U.S. | 2015 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.8 | ||
| U.S. | 2016 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 8.1 | ||
| U.S. | 2017 | 8.4 | 8.3 | 8.5 | ||
Data Notes
Parkinson's disease cause of death ICD 10 codes G20-G21.[[br]] Rates are age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Sources
- Utah Death Certificate Database, Office of Vital Records and Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
- U.S. Underlying Cause of Death Data: WONDER Online Database. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Accessed at [http://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10.html]
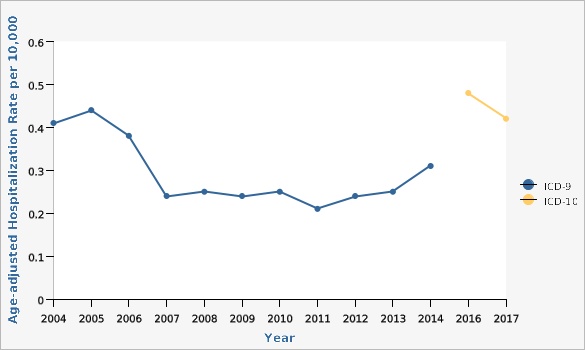
| ICD-9 vs. ICD-10 | Year | Crude Hospitalization Rate per 10,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 13 | ||||||
| ICD-9 | 2004 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.36 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2005 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 0.39 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2006 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.35 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2007 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.23 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2008 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.25 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2009 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.25 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2010 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.25 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2011 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.23 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2012 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.25 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2013 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.27 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2014 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.33 | ||
| ICD-10 | 2016 | 0.41 | 0.34 | 0.49 | ||
| ICD-10 | 2017 | 0.36 | 0.29 | 0.43 | ||
Data Notes
Parkinson's disease was defined by ICD9 code 332 from 2004-2014 and ICD10 codes G20-G21 from 2016-2017. The increase in hospitalizations is likely due to this change.[[br]] Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
Utah Inpatient Hospital Discharge Data, Office of Health Care Statistics, Utah Department of Health| Utah vs. U.S. | Year | Crude Death Rate per 100,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 38 | ||||||
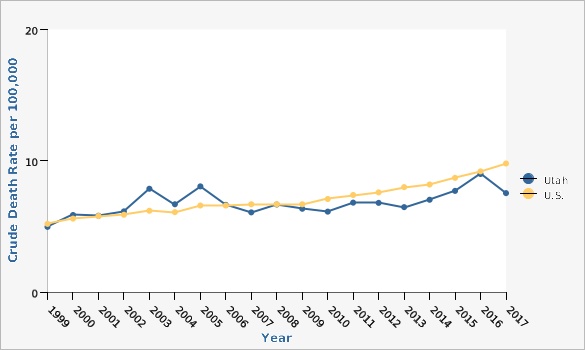
| Utah | 1999 | 5.0 | 4.1 | 6.0 | ||
| Utah | 2000 | 5.9 | 4.9 | 7.0 | ||
| Utah | 2001 | 5.8 | 4.9 | 6.9 | ||
| Utah | 2002 | 6.2 | 5.2 | 7.2 | ||
| Utah | 2003 | 7.9 | 6.8 | 9.1 | ||
| Utah | 2004 | 6.7 | 5.7 | 7.8 | ||
| Utah | 2005 | 8.1 | 7.0 | 9.3 | ||
| Utah | 2006 | 6.6 | 5.7 | 7.7 | ||
| Utah | 2007 | 6.1 | 5.2 | 7.1 | ||
| Utah | 2008 | 6.7 | 5.7 | 7.7 | ||
| Utah | 2009 | 6.4 | 5.4 | 7.4 | ||
| Utah | 2010 | 6.1 | 5.2 | 7.1 | ||
| Utah | 2011 | 6.8 | 5.9 | 7.9 | ||
| Utah | 2012 | 6.8 | 5.9 | 7.8 | ||
| Utah | 2013 | 6.5 | 5.6 | 7.5 | ||
| Utah | 2014 | 7.0 | 6.1 | 8.1 | ||
| Utah | 2015 | 7.7 | 6.7 | 8.8 | ||
| Utah | 2016 | 9.0 | 8.0 | 10.1 | ||
| Utah | 2017 | 7.5 | 6.6 | 8.6 | ||
| U.S. | 1999 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 5.3 | ||
| U.S. | 2000 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.7 | ||
| U.S. | 2001 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 5.9 | ||
| U.S. | 2002 | 5.9 | 5.8 | 6.0 | ||
| U.S. | 2003 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 6.3 | ||
| U.S. | 2004 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 6.2 | ||
| U.S. | 2005 | 6.6 | 6.5 | 6.7 | ||
| U.S. | 2006 | 6.6 | 6.5 | 6.6 | ||
| U.S. | 2007 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.8 | ||
| U.S. | 2008 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.8 | ||
| U.S. | 2009 | 6.7 | 6.6 | 6.8 | ||
| U.S. | 2010 | 7.1 | 7.0 | 7.2 | ||
| U.S. | 2011 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.5 | ||
| U.S. | 2012 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 7.7 | ||
| U.S. | 2013 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 8.1 | ||
| U.S. | 2014 | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.3 | ||
| U.S. | 2015 | 8.7 | 8.6 | 8.8 | ||
| U.S. | 2016 | 9.2 | 9.1 | 9.3 | ||
| U.S. | 2017 | 9.8 | 9.7 | 9.9 | ||
Data Notes
Parkinson's disease cause of death ICD 10 codes G20-G21.Data Sources
- Utah Death Certificate Database, Office of Vital Records and Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
- U.S. Underlying Cause of Death Data: WONDER Online Database. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Accessed at [http://wonder.cdc.gov/ucd-icd10.html]
| Age-adjusted Death Rate per 100,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 2 | ||||||
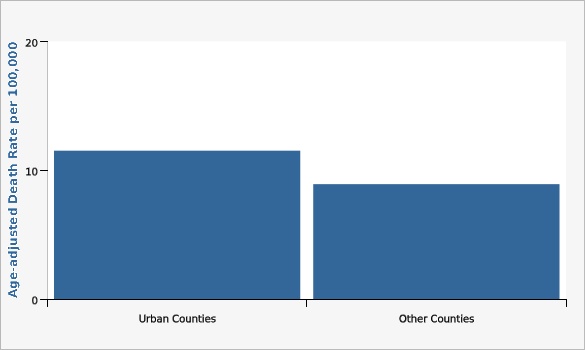
| Urban Counties | 11.5 | 10.6 | 12.5 | |||
| Other Counties | 8.9 | 7.7 | 10.3 | |||
Data Notes
Parkinson's disease cause of death ICD 10 codes G20-G21.[[br]] Urban counties include Davis, Salt Lake, Utah and Weber Counties.[[br]] Age-adjusted to the 2000 U.S. standard population.Data Sources
- Utah Death Certificate Database, Office of Vital Records and Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2016
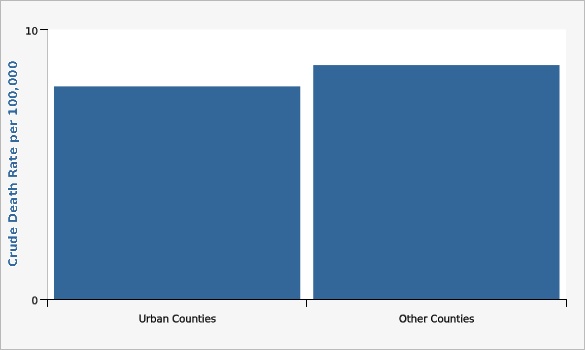
| Crude Death Rate per 100,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 2 | ||||||
| Urban Counties | 7.9 | 7.2 | 8.6 | |||
| Other Counties | 8.7 | 7.5 | 10.0 | |||
Data Notes
Urban counties include Davis, Salt Lake, Utah and Weber Counties.[[br]] Parkinson's disease cause of death ICD 10 codes G20-G21.Data Sources
- Utah Death Certificate Database, Office of Vital Records and Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
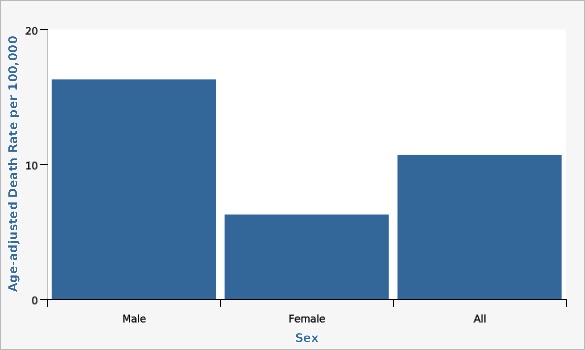
| Sex | Age-adjusted Death Rate per 100,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Male | 16.3 | 14.9 | 17.8 | |||
| Female | 6.3 | 5.5 | 7.1 | |||
| All | 10.7 | 9.9 | 11.5 | |||
Data Notes
Parkinson's disease cause of death ICD 10 codes G20-G21.Data Sources
- Utah Death Certificate Database, Office of Vital Records and Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
Men have crude rates of death for Parkinson's disease as the underlying cause of death are almost twice the rate for women.
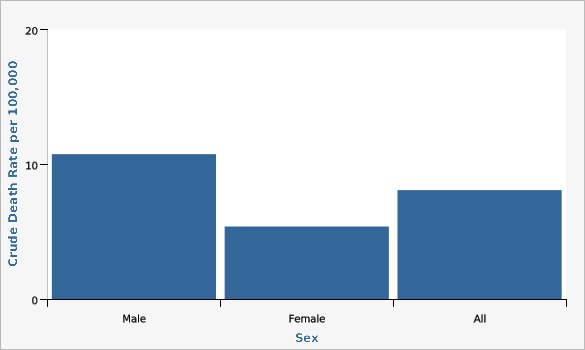
| Sex | Crude Death Rate per 100,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Male | 10.8 | 9.8 | 11.7 | |||
| Female | 5.4 | 4.7 | 6.1 | |||
| All | 8.1 | 7.5 | 8.7 | |||
Data Notes
Three years of data were combined to get reliable estimates.[[br]] Parkinson's disease cause of death ICD 10 codes G20-G21.Data Sources
- Utah Death Certificate Database, Office of Vital Records and Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
Age-adjusted rates of hospital discharges with Parkinson's Disease as the primary diagnosis declined from 2004 until about 2013, where they began to increase again.
| ICD-9 vs. ICD-10 | Year | Age-adjusted Hospitalization Rate per 10,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 13 | ||||||
| ICD-9 | 2004 | 0.41 | 0.32 | 0.52 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2005 | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0.55 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2006 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.48 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2007 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.33 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2008 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.33 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2009 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.32 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2010 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.33 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2011 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.29 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2012 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.32 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2013 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.32 | ||
| ICD-9 | 2014 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.39 | ||
| ICD-10 | 2016 | 0.48 | 0.4 | 0.58 | ||
| ICD-10 | 2017 | 0.42 | 0.34 | 0.5 | ||
Data Notes
Parkinson's disease was defined by ICD9 code 332 from 2004-2014 and ICD10 codes G20-G21 from 2016-2017. The increase in hospitalizations is likely due to this change.[[br]] Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Sources
- Utah Inpatient Hospital Discharge Data, Office of Health Care Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
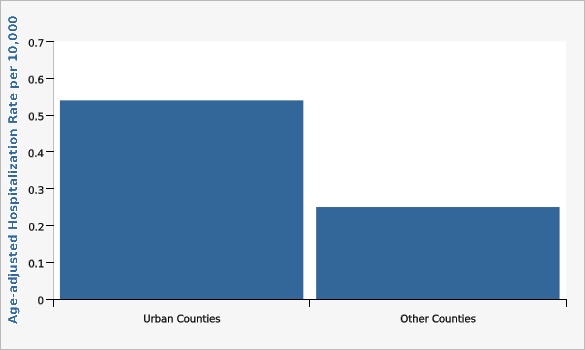
Utah residents in urban (Davis, Salt Lake, Utah and Weber) counties had higher rates of hospitalizations for Parkinson's Disease than residents in rural counties.
| Age-adjusted Hospitalization Rate per 10,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 2 | ||||||
| Urban Counties | 0.54 | 0.47 | 0.63 | |||
| Other Counties | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.34 | |||
Data Notes
Two years of data (2016-2017) were combined to show the age-adjusted rates of discharges for urban vs. rural counties.[[br]] Urban counties include Davis, Salt Lake, Utah and Weber Counties.[[br]] Parkinson's disease defined by ICD 10 codes G20,G21.[[br]] Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Sources
- Utah Inpatient Hospital Discharge Data, Office of Health Care Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
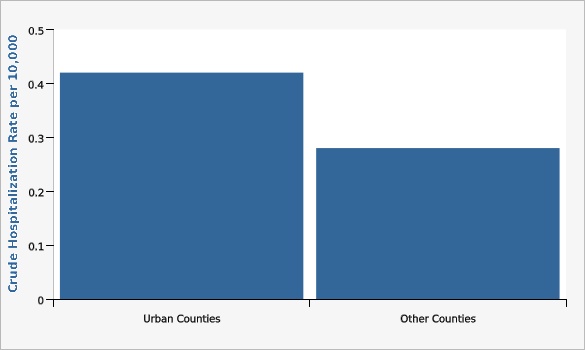
Utah residents in urban (Davis, Salt Lake, Utah and Weber) counties had higher rates of hospitalizations for Parkinson's Disease than residents in rural counties.
| Crude Hospitalization Rate per 10,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 2 | ||||||
| Urban Counties | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.48 | |||
| Other Counties | 0.28 | 0.2 | 0.38 | |||
Data Notes
Two years of data (2016-2017) were combined to show the crude rates of discharges for urban vs. rural counties.[[br]] Urban counties include Davis, Salt Lake, Utah and Weber Counties.[[br]] Parkinson's disease defined by ICD 10 codes G20,G21.Data Sources
- Utah Inpatient Hospital Discharge Data, Office of Health Care Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
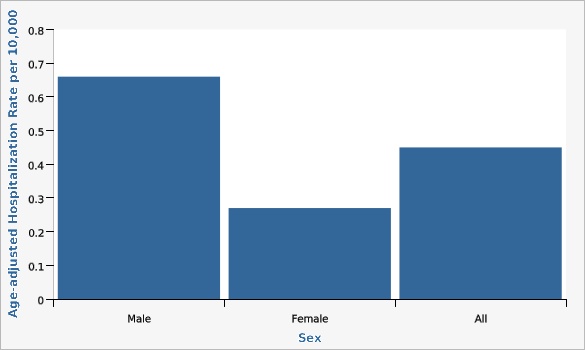
| Sex | Age-adjusted Hospitalization Rate per 10,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Male | 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.77 | |||
| Female | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.34 | |||
| All | 0.45 | 0.39 | 0.51 | |||
Data Notes
Two years of data (2016-2017) were combined to show the age-adjusted rates of discharges.[[br]] Parkinson's disease defined by ICD 10 codes G20,G21.[[br]] Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Sources
- Utah Inpatient Hospital Discharge Data, Office of Health Care Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
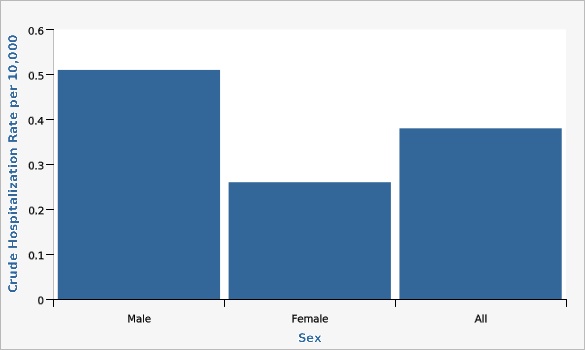
| Sex | Crude Hospitalization Rate per 10,000 | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Male | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.6 | |||
| Female | 0.26 | 0.2 | 0.32 | |||
| All | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.44 | |||
Data Notes
Two years of data (2016-2017) were combined to show the crude rates of discharges.[[br]] Parkinson's disease defined by ICD 10 codes G20,G21.[[br]] Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Sources
- Utah Inpatient Hospital Discharge Data, Office of Health Care Statistics, Utah Department of Health
- Population Estimates: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2017
References and Community Resources
Ahlskog, J. Eric, Aerobic Exercise: Evidence for a Direct Brain Effect to Slow Parkinson Disease Progression. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, Volume 93, Issue 3 , 360 - 372. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Stats of the States' available at: [https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/pressroom/sosmap/parkinsons_disease_mortality/parkinsons_disease.htm]. Combs, Stephanie A., Diehl, M. Dyer, Staples, William H., Conn, Lindsay, Davis, Kendra, Lewis, Nicole, Schaneman, Katie; January 2011. Boxing Training for Patients With Parkinson Disease: A Case Series, Physical Therapy, Volume 91, Issue 1, 1 Pages 132-142, [https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20100142]. Connolly BS, Lang AE. Pharmacological Treatment of Parkinson Disease A Review. JAMA. 2014;311(16):1670-1683. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3654. Dance for PD. Available at: [https://danceforparkinsons.org/resources/research]. Michael J. Fox Parkinson's Foundation - available at: [https://www.michaeljfox.org/understanding-parkinsons/living-with-pd/topic.php?deep-brain-stimulation]. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Available at: [https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Parkinsons-Disease-Information-Page]. Parkinson's Foundation - available at: [http://parkinson.org/Understanding-Parkinsons/Causes-and-Statistics/Statistics]. Salgado S, Williams N, Kotian R, Salgado M. An Evidence-Based Exercise Regimen for Patients with Mild to Moderate Parkinson's Disease. Brain Sciences. 2013;3(1):87-100. doi:10.3390/brainsci3010087. Willis, A.W., Schootman, M., Evanoff, B.A., Perlmutter, J.S., Racette, B.A. 2011 Aug 30. Neurologist care in Parkinson disease: A utilization, outcomes, and survival study Neurology; 77(9): 851-857. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31822c9123.More Resources and Links
Evidence-based community health improvement ideas and interventions may be found at the following sites:- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) WONDER Database, a system for disseminating public health data and information.
- United States Census Bureau data dashboard.
- Utah healthy Places Index, evidence-based and peer-reviewed tool, supports efforts to prioritize equitable community investments, develop critical programs and policies across the state, and much more.
- County Health Rankings
- Kaiser Family Foundation's StateHealthFacts.org
- Medical literature can be queried at PubMed library.
Page Content Updated On 07/24/2019,
Published on 12/26/2019