Complete Health Indicator Report of Breast Cancer Screening (Mammography)
Definition
The proportion of women 40 years or older who reported having a mammogram in the last two years.Numerator
The number of women 40 years or older who reported having a mammogram in the last two years.Denominator
The total number of female survey respondents aged 40 or older excluding those who responded "don't know" or "refused" to the numerator question.Data Interpretation Issues
In 2016, age distribution was changed from 8 groupings to 5 groupings; this may affect the interpretation of data trends.Why Is This Important?
Breast cancer is the most commonly occurring cancer in U.S. women (excluding skin cancers) and the leading cause of female cancer death in Utah. Deaths from breast cancer can be substantially reduced if the tumor is discovered at an early stage. Mammography is currently the best method for detecting cancer early. A mammogram is a noninvasive x-ray used to look for early signs of breast cancer. Clinical trials and observational studies have demonstrated that routine screening with mammography can reduce breast cancer mortality by roughly 20% for women of average risk.^1^ The American College of Radiology (ACR) and Society of Breast Imaging (SBI) recommend getting annual mammograms starting at age 40 for women of average risk, but earlier and more intensive screening for high-risk patients.^2^ Significant scientific evidence has demonstrated that this approach saves more lives than delayed or less frequent screening.^3^[[br]] [[br]] ---- 1. Myers ER, Moorman P, Gierisch JM, et al. Benefits and harms of breast cancer screening. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.13183.[[br]] 2. D.L. Monticciolo et al. Breast cancer screening in women at higher-than-average risk: recommendations from the ACR. J Am Coll Radiol, 20 (9) (2023), pp. 902-914.[[br]] 3. American College of Radiology Committee on BI-RADS. Mammography Saves Lives. Available at: [https://www.acr.org/Practice-Management-Quality-Informatics/Practice-Toolkit/Patient-Resources/Mammography-Saves-Lives]. Accessed on January 1, 2023.Other Objectives
CSTE Chronic Disease IndicatorsHow Are We Doing?
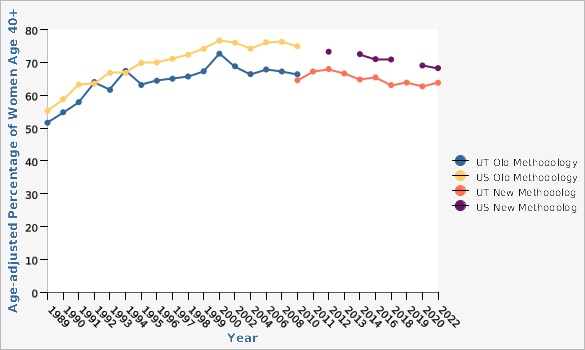
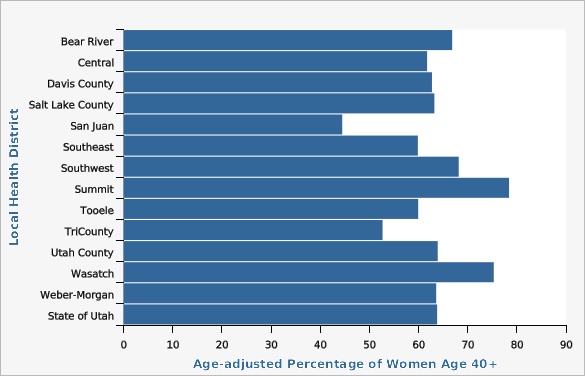
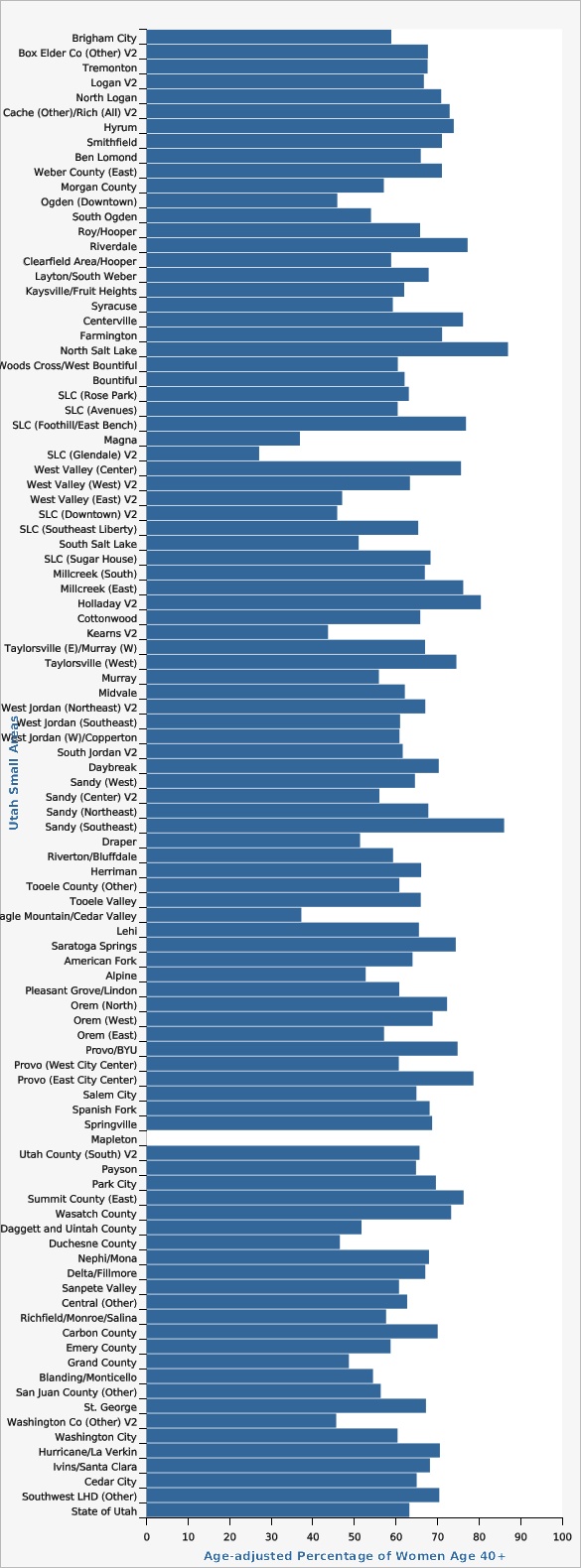
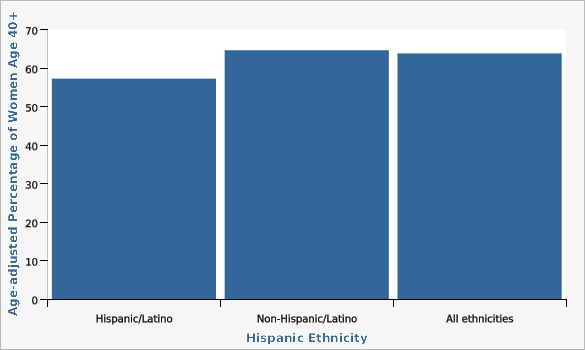
Between 1989 and 2022, the percentage of Utah women aged 40 or older who reported receiving a mammogram within the last two years increased from 51.6% to 63.8%. Although rates have increased some over time, the rate in Utah still falls far below the national average. In 2022, the mammography screening rate in Utah was significantly lower than the U.S. rate of 68.2%. Utah is ranked 44th in the nation for mammography screening. In 2022, the percentage of women who received a mammogram in TriCounty Local Health District (52.7%) was statistically significantly lower than the state average (63.8%). Conversely, the screening rate in Summit County Local Health District (78.4%) was significantly higher than the overall rate in Utah. See additional data views for more specific geographic differences between the Utah Small Areas. For the same year, there were no significant differences in mammography screening rates between Hispanic and non-Hispanic ethnic groups, nor were there any significant differences in rates among different racial groups for combined data years 2018, 2019, 2020, and 2022. Mammography rates generally tend to increase with age, education level, and amount of household income increases. In 2020 and 2022 combined, women age 40-49 had significantly lower rates of mammography screening (52.4%) than older women (69.3%; most likely due to differing guidelines concerning the age at which breast cancer screening should begin). Looking at the level of education completed for the same time period, college graduates were significantly more likely to have received a mammogram (67.8%) than the general population (63.3%), whereas the screening rate among women who had not completed high school was significantly lower than the state average at just 53.4%. In the same timeframe, women in households with an annual income of less than $25,000 were significantly less likely to have had a mammogram in the past two years (50.9%) compared to other women, whereas women in households with an annual income of more than $75,000 were more likely to have had a mammogram in the past two years (68.4%).How Do We Compare With the U.S.?
Nationally, the percentage of women aged 40 or older who reported receiving a mammogram in the past two years increased from 55.2% in 1989 to 68.2% in 2022. Since 1994, the mammography screening rate in Utah has consistently fallen below the U.S. rate. In 2022, only 63.8% of Utah women aged 40 and older had received a mammogram in the last two years compared with 68.2% of U.S. women. Utah is ranked 44th in the nation for mammography screening.What Is Being Done?
The Utah Breast & Cervical Cancer Program (Utah B&C) partners with local health departments, community clinics, hospitals, and healthcare professionals to help those with low incomes who do not have adequate insurance gain access to timely breast and cervical cancer screening, diagnostic and treatment services. Eligible women can apply to Utah B&C by calling 800-717-1811 or by submitting an online enrollment form available at: [https://cancerutah.org/do-i-qualify/]. The Utah Cancer Coalition is a statewide partnership whose goal is to reduce the burden of cancer. The mission of the coalition is to lower cancer incidence and mortality in Utah through collaborative efforts directed toward cancer prevention and control. As a result of this planning process, objectives and strategies have been developed by community partners regarding the early detection of cervical, testicular, prostate, skin, breast, and colorectal cancers as well as the promotion of physical activity, healthy eating habits, and smoking cessation.Available Services
The Utah Breast & Cervical Cancer Program (Utah B&C) partners with local health departments, community clinics, hospitals, and healthcare professionals to help those with low incomes who do not have adequate insurance gain access to timely breast and cervical cancer screening, diagnostic and treatment services. Eligible women can apply to Utah B&C by calling 800-717-1811 or by submitting an online enrollment form available at: [https://cancerutah.org/do-i-qualify/].Health Program Information
In 1980, the Utah Department of Health and Human Services began providing clinical breast exams and a sliding fee scale. In 1993, state funding was appropriated for mammography. That same year, the Utah Breast and Cervical Cancer Program (Utah B&C) first received a capacity-building grant from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to conduct breast and cervical cancer screening in Utah. A comprehensive grant was awarded to the program in 1994 to continue breast and cervical cancer screening. Since 1994, Utah B&C and partners, including local health departments, mammography facilities, pathology laboratories, and private providers, have worked together to ensure the appropriate and timely provision of clinical services. Utah B&C continues to receive funding from the CDC for breast and cervical cancer screening.Related Indicators
Relevant Population Characteristics
Routine screening for breast cancer with mammography has been identified as a priority issue for women 40 years of age or older by several health organizations.Related Relevant Population Characteristics Indicators:
- Utah Population Characteristics: Age Distribution of the Population
- Breast Cancer Deaths
- Breast Cancer Incidence
- Breast Cancer Screening (Mammography)
- Cancer Deaths
- Cervical Cancer Death
- Cervical cancer incidence
- Cervical Cancer Screening (Pap)
- Cost as a Barrier to Health Care
- Utah Population Characteristics: Education Level in the Population
- Utah Population Characteristics: Household Income
- No Health Insurance Coverage
- Obesity Among Adults
- Utah Population Characteristics: Poverty, All Persons
Health Care System Factors
According to data collected by the Utah Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, use of mammography is lower among women without health insurance compared to women with health insurance. Mammography is a preventive service covered by Medicare.Related Health Care System Factors Indicators:
Risk Factors
The most important risk factor for breast cancer is increasing age. Other established risk factors include personal or family history of breast cancer, history of abnormal breast biopsy, genetic alterations, early age at onset of menses, late age at onset of menopause, never having children or having a first live birth at age 30 or older, and history of exposure to high dose radiation. Associations have also been suggested between breast cancer and oral contraceptives, long-term use of hormone replacement therapy, obesity (in post-menopausal women), alcohol, and a diet high in fat. Some studies suggest that exercise in youth might give life-long protection against breast cancer and that even moderate physical activity as an adult could lower breast cancer risk. More research is needed to confirm these findings.Related Risk Factors Indicators:
- Daily Fruit Consumption
- Daily Vegetable Consumption
- Utah Population Characteristics: Age Distribution of the Population
- Alcohol Consumption - Binge Drinking
- Alcohol Consumption - Heavy Drinking
- Obesity Among Adults
- Overweight or Obese
- Physical Activity: Recommended Aerobic Activity Among Adults
- Physical Activity Among Adolescents
Health Status Outcomes
Routine screening with mammography is an important tool in the early detection of breast cancer and early detection can save lives.Related Health Status Outcomes Indicators:
Graphical Data Views
| BRFSS Utah vs. U.S. | Year | Age-adjusted Percentage of Women Age 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 50 | ||||||
| UT Old Methodology | 1989 | 51.6% | 46.6% | 56.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1990 | 54.8% | 50.0% | 59.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1991 | 57.9% | 53.1% | 62.8% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1992 | 64.0% | 59.7% | 68.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1993 | 61.6% | 56.9% | 66.2% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1994 | 67.4% | 62.7% | 72.0% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1995 | 63.1% | 58.9% | 67.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1996 | 64.4% | 60.7% | 68.2% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1997 | 65.0% | 60.7% | 69.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1998 | 65.7% | 61.3% | 70.1% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 1999 | 67.3% | 63.3% | 71.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2000 | 72.6% | 68.9% | 76.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2002 | 68.8% | 65.5% | 72.0% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2004 | 66.4% | 63.7% | 69.1% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2006 | 67.8% | 65.3% | 70.2% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2008 | 67.2% | 64.5% | 69.8% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2010 | 66.4% | 64.5% | 68.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1989 | 55.2% | 54.1% | 56.3% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1990 | 58.8% | 57.7% | 59.8% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1991 | 63.2% | 62.3% | 64.1% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1992 | 63.5% | 62.7% | 64.3% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1993 | 66.8% | 56.9% | 66.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1994 | 66.8% | 66.0% | 67.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1995 | 69.8% | 69.0% | 70.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1996 | 70.0% | 69.3% | 70.6% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1997 | 71.1% | 70.4% | 71.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1998 | 72.3% | 71.0% | 73.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 1999 | 74.1% | 73.5% | 74.6% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2000 | 76.6% | 76.0% | 77.1% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2002 | 76.0% | 75.4% | 76.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2004 | 74.2% | 73.8% | 74.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2006 | 76.1% | 75.7% | 76.6% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2008 | 76.2% | 75.9% | 76.6% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2010 | 74.9% | 74.5% | 75.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2010 | 64.5% | 62.6% | 66.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2011 | 67.2% | 64.4% | 69.9% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2012 | 68.0% | 66.2% | 69.7% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2013 | 66.6% | 63.7% | 69.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2014 | 64.8% | 63.1% | 66.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2016 | 65.4% | 63.3% | 67.5% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2018 | 63.1% | 61.0% | 65.1% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2019 | 63.8% | 60.9% | 66.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2020 | 62.7% | 60.6% | 64.7% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2022 | 63.8% | 61.6% | 65.9% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2012 | 73.2% | 72.8% | 73.7% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2014 | 72.5% | 72.1% | 72.9% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2016 | 71.0% | 70.5% | 71.5% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2018 | 70.9% | 70.3% | 71.4% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2020 | 69.0% | 68.4% | 69.7% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2022 | 68.2% | 67.7% | 68.8% | ||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population. Data provided for all years available. Old Methodology: Previous BRFSS methodology used "post-stratification" which was used to weight data by age, gender, and local health district (LHD). New Methodology: To reduce bias and more accurately represent population data, the BRFSS has changed survey methodology. It began conducting surveys by cellular phone in addition to landline phones. It also adopted "iterative proportional fitting" (raking) as its weighting method. With raking, education, race/ethnicity, marital status, home ownership/renter, and telephone source are included in the weighting procedure. Due to changes in sampling and weighting methodology, data from the new methodology represents a new baseline, and comparisons from new to old methodology data are not appropriate.Data Sources
- Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]
- Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey Data, US Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
| Local Health District | Age-adjusted Percentage of Women Age 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 14 | ||||||
| Bear River | 66.8% | 58.0% | 74.6% | |||
| Central | 61.8% | 51.4% | 71.1% | |||
| Davis County | 62.7% | 55.7% | 69.3% | |||
| Salt Lake County | 63.2% | 59.1% | 67.1% | |||
| San Juan | 44.5% | 23.8% | 67.2% | |||
| Southeast | 59.9% | 49.0% | 69.9% | |||
| Southwest | 68.2% | 60.4% | 75.1% | |||
| Summit | 78.4% | 64.9% | 87.7% | |||
| Tooele | 59.9% | 50.9% | 68.3% | |||
| TriCounty | 52.7% | 42.4% | 62.7% | |||
| Utah County | 63.9% | 58.6% | 68.9% | |||
| Wasatch | 75.3% | 63.3% | 84.4% | |||
| Weber-Morgan | 63.6% | 56.7% | 70.0% | |||
| State of Utah | 63.8% | 61.6% | 65.9% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]| Utah Small Areas | Age-adjusted Percentage of Women Age 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 100 | ||||||
| Brigham City | 58.9% | 44.3% | 72.0% | |||
| Box Elder Co (Other) V2 | 67.7% | 49.7% | 81.6% | * | ||
| Tremonton | 67.6% | 48.4% | 82.3% | |||
| Logan V2 | 66.7% | 54.4% | 77.1% | |||
| North Logan | 70.9% | 52.6% | 84.3% | |||
| Cache (Other)/Rich (All) V2 | 72.9% | 58.4% | 83.8% | |||
| Hyrum | 73.9% | 45.8% | 90.5% | * | ||
| Smithfield | 71.1% | 52.4% | 84.6% | * | ||
| Ben Lomond | 66.0% | 56.1% | 74.7% | |||
| Weber County (East) | 71.1% | 58.1% | 81.3% | |||
| Morgan County | 57.1% | 32.5% | 78.6% | |||
| Ogden (Downtown) | 45.9% | 34.9% | 57.3% | |||
| South Ogden | 54.0% | 41.6% | 65.9% | |||
| Roy/Hooper | 65.8% | 53.0% | 76.7% | |||
| Riverdale | 77.3% | 63.5% | 86.9% | |||
| Clearfield Area/Hooper | 58.9% | 47.7% | 69.2% | |||
| Layton/South Weber | 67.9% | 58.3% | 76.2% | |||
| Kaysville/Fruit Heights | 62.0% | 49.3% | 73.3% | |||
| Syracuse | 59.3% | 45.3% | 71.9% | |||
| Centerville | 76.2% | 61.6% | 86.4% | |||
| Farmington | 71.1% | 51.6% | 85.0% | * | ||
| North Salt Lake | 87.0% | 69.4% | 95.2% | * | ||
| Woods Cross/West Bountiful | 60.5% | 38.1% | 79.2% | * | ||
| Bountiful | 62.1% | 50.0% | 72.9% | |||
| SLC (Rose Park) | 63.1% | 44.6% | 78.4% | * | ||
| SLC (Avenues) | 60.4% | 43.9% | 74.9% | |||
| SLC (Foothill/East Bench) | 76.9% | 54.8% | 90.1% | * | ||
| Magna | 36.9% | 23.8% | 52.4% | |||
| SLC (Glendale) V2 | 27.1% | 11.1% | 52.6% | * | ||
| West Valley (Center) | 75.7% | 60.4% | 86.4% | |||
| West Valley (West) V2 | 63.4% | 46.6% | 77.5% | |||
| West Valley (East) V2 | 47.1% | 31.4% | 63.4% | |||
| SLC (Downtown) V2 | 45.9% | 30.5% | 62.1% | |||
| SLC (Southeast Liberty) | 65.4% | 43.0% | 82.6% | |||
| South Salt Lake | 51.0% | 27.0% | 74.6% | |||
| SLC (Sugar House) | 68.3% | 55.6% | 78.8% | |||
| Millcreek (South) | 67.0% | 52.7% | 78.7% | |||
| Millcreek (East) | 76.2% | 62.2% | 86.2% | |||
| Holladay V2 | 80.4% | 63.2% | 90.8% | * | ||
| Cottonwood | 65.9% | 52.4% | 77.2% | |||
| Kearns V2 | 43.7% | 29.6% | 58.9% | |||
| Taylorsville (E)/Murray (W) | 67.0% | 52.1% | 79.2% | |||
| Taylorsville (West) | 74.6% | 62.1% | 84.0% | |||
| Murray | 55.9% | 41.2% | 69.7% | |||
| Midvale | 62.2% | 45.1% | 76.6% | |||
| West Jordan (Northeast) V2 | 67.1% | 49.7% | 80.8% | |||
| West Jordan (Southeast) | 61.0% | 45.4% | 74.6% | |||
| West Jordan (W)/Copperton | 60.9% | 44.6% | 75.1% | |||
| South Jordan V2 | 61.6% | 48.4% | 73.4% | |||
| Daybreak | 70.3% | 54.6% | 82.3% | |||
| Sandy (West) | 64.6% | 46.9% | 79.0% | * | ||
| Sandy (Center) V2 | 56.0% | 42.3% | 68.9% | |||
| Sandy (Northeast) | 67.8% | 47.5% | 83.1% | * | ||
| Sandy (Southeast) | 86.0% | 73.4% | 93.2% | * | ||
| Draper | 51.4% | 37.1% | 65.5% | |||
| Riverton/Bluffdale | 59.3% | 44.9% | 72.4% | |||
| Herriman | 66.1% | 51.3% | 78.3% | |||
| Tooele County (Other) | 60.8% | 44.6% | 75.0% | |||
| Tooele Valley | 66.0% | 57.7% | 73.4% | |||
| Eagle Mountain/Cedar Valley | 37.3% | 25.1% | 51.3% | |||
| Lehi | 65.6% | 53.6% | 75.8% | |||
| Saratoga Springs | 74.4% | 60.0% | 85.0% | |||
| American Fork | 64.0% | 51.3% | 75.0% | |||
| Alpine | 52.7% | 41.0% | 64.2% | * | ||
| Pleasant Grove/Lindon | 60.8% | 50.4% | 70.4% | |||
| Orem (North) | 72.3% | 55.9% | 84.3% | |||
| Orem (West) | 68.8% | 51.0% | 82.4% | |||
| Orem (East) | 57.2% | 44.0% | 69.4% | |||
| Provo/BYU | 74.8% | 61.9% | 84.5% | |||
| Provo (West City Center) | 60.7% | 44.7% | 74.7% | |||
| Provo (East City Center) | 78.7% | 58.8% | 90.5% | * | ||
| Salem City | 65.0% | 47.7% | 79.0% | |||
| Spanish Fork | 68.1% | 55.7% | 78.4% | |||
| Springville | 68.7% | 54.9% | 79.9% | |||
| Mapleton | ** | ** | ||||
| Utah County (South) V2 | 65.7% | 49.3% | 79.0% | * | ||
| Payson | 64.8% | 50.0% | 77.3% | |||
| Park City | 69.6% | 56.5% | 80.2% | |||
| Summit County (East) | 76.3% | 62.6% | 86.1% | |||
| Wasatch County | 73.3% | 64.1% | 80.8% | |||
| Daggett and Uintah County | 51.7% | 42.4% | 61.0% | |||
| Duchesne County | 46.5% | 35.1% | 58.4% | |||
| Nephi/Mona | 68.0% | 41.2% | 86.5% | * | ||
| Delta/Fillmore | 67.1% | 48.1% | 81.8% | * | ||
| Sanpete Valley | 60.8% | 46.4% | 73.4% | |||
| Central (Other) | 62.7% | 52.0% | 72.3% | |||
| Richfield/Monroe/Salina | 57.6% | 43.8% | 70.4% | |||
| Carbon County | 70.1% | 58.9% | 79.3% | |||
| Emery County | 58.7% | 48.5% | 68.3% | |||
| Grand County | 48.7% | 32.5% | 65.2% | |||
| Blanding/Monticello | 54.5% | 40.6% | 67.7% | |||
| San Juan County (Other) | 56.4% | 29.5% | 80.0% | * | ||
| St. George | 67.2% | 56.6% | 76.4% | |||
| Washington Co (Other) V2 | 45.6% | 33.6% | 58.2% | |||
| Washington City | 60.4% | 43.0% | 75.5% | |||
| Hurricane/La Verkin | 70.6% | 55.3% | 82.3% | |||
| Ivins/Santa Clara | 68.2% | 39.2% | 87.7% | * | ||
| Cedar City | 65.0% | 52.0% | 76.1% | |||
| Southwest LHD (Other) | 70.4% | 57.6% | 80.7% | |||
| State of Utah | 63.2% | 61.7% | 64.8% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population. *Use caution in interpreting; the estimate has a coefficient of variation >30% and is therefore deemed unreliable by Utah Department of Health and Human Services standards. **The estimate has been suppressed because the relative standard error is greater than 50% or the observed number of events is very small and not appropriate for publication. Small area groupings were changed in 2018 to better reflect the boundaries of those areas. This may affect interpretation of trend data. Methods and changes to Utah Small Areas may be found on IBIS at the following URL: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/resource/Guidelines.html].Data Source
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]| Hispanic Ethnicity | Age-adjusted Percentage of Women Age 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Hispanic/Latino | 57.2% | 49.2% | 64.9% | |||
| Non-Hispanic/Latino | 64.6% | 62.3% | 66.9% | |||
| All ethnicities | 63.8% | 61.6% | 65.9% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
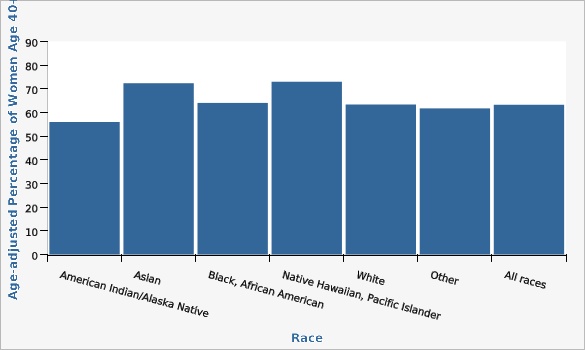
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]| Race | Age-adjusted Percentage of Women Age 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 7 | ||||||
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 56.0% | 44.3% | 67.1% | |||
| Asian | 72.4% | 60.7% | 81.6% | |||
| Black, African American | 64.0% | 51.0% | 75.3% | |||
| Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islander | 73.0% | 56.4% | 85.0% | |||
| White | 63.4% | 62.2% | 64.5% | |||
| Other | 61.7% | 55.6% | 67.6% | |||
| All races | 63.3% | 62.1% | 64.4% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to the U.S. 2000 standard population using 3 age groups.Data Source
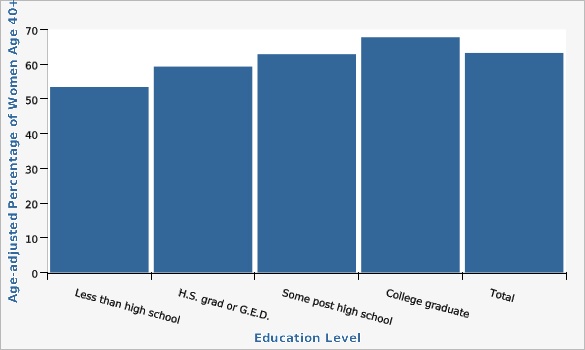
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]| Education Level | Age-adjusted Percentage of Women Age 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| Less than high school | 53.4% | 45.8% | 60.9% | |||
| H.S. grad or G.E.D. | 59.3% | 55.9% | 62.6% | |||
| Some post high school | 62.9% | 60.3% | 65.4% | |||
| College graduate | 67.8% | 65.6% | 69.9% | |||
| Total | 63.2% | 61.7% | 64.8% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
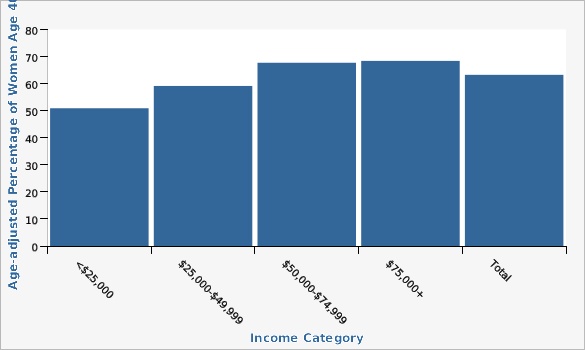
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]| Income Category | Age-adjusted Percentage of Women Age 40+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| <$25,000 | 50.9% | 45.4% | 56.3% | |||
| $25,000-$49,999 | 59.1% | 54.8% | 63.3% | |||
| $50,000-$74,999 | 67.7% | 63.6% | 71.6% | |||
| $75,000+ | 68.4% | 66.1% | 70.6% | |||
| Total | 63.2% | 61.7% | 64.8% | |||
Data Notes
Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
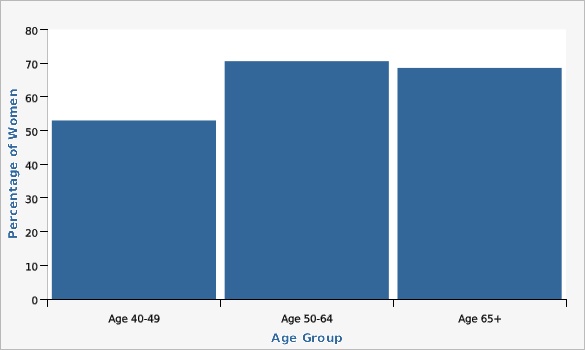
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]| Age Group | Percentage of Women | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Age 40-49 | 53.0% | 48.7% | 57.3% | |||
| Age 50-64 | 70.6% | 67.0% | 73.9% | |||
| Age 65+ | 68.6% | 65.2% | 71.9% | |||
Data Source
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]References and Community Resources
Utah Breast & Cervical Cancer Screening Program @ https://cancer.utah.gov/][[br]] Utah Cancer Coalition @ [https://utahcancercoalition.org/][[br]] Susan G. Komen Foundation @ [http://www.komen.org][[br]] National Cancer Institute @ [http://www.cancer.gov][[br]] American Cancer Society @ [http://www.cancer.org][[br]] Huntsman Cancer Institute @ [http://huntsmancancer.org][[br]] Centers for Disease Control and Prevention @ [http://www.cdc.gov][[br]] American Society of Clinical Oncology @ [http://www.asco.org][[br]]More Resources and Links
Evidence-based community health improvement ideas and interventions may be found at the following sites:- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) WONDER Database, a system for disseminating public health data and information.
- United States Census Bureau data dashboard.
- Utah healthy Places Index, evidence-based and peer-reviewed tool, supports efforts to prioritize equitable community investments, develop critical programs and policies across the state, and much more.
- County Health Rankings
- Kaiser Family Foundation's StateHealthFacts.org
- Medical literature can be queried at PubMed library.
Page Content Updated On 03/26/2024,
Published on 04/11/2024