PHOM Indicator Profile Report of Life Expectancy at Birth
Why Is This Important?
Life expectancy is a measure that is often used to gauge the overall health of a community. Life expectancy at birth measures health status across all age groups. Shifts in life expectancy are often used to describe trends in mortality. Being able to predict how populations will age has enormous implications for the planning and provision of services and support. Small increases in life expectancy translate into large increases in the population. As the life expectancy of a population lengthens, the number of people living with chronic illnesses tends to increase because chronic illnesses are more common among older persons.Life expectancy at birth by sex, Utah and U.S., 2021 1980-2022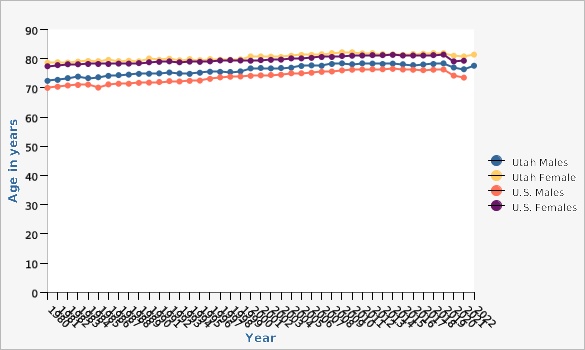 |
In Utah, life expectancy at birth for males increased from 72.4 years in 1980 to 77.6 years in 2022, and for females from 78.6 to 81.4 years. In comparison, life expectancy at birth in the U.S. rose from 70.0 to 73.5 years for males, and from 77.4 to 79.3 years for females (from 1980 to 2021).
Data Sources
- Utah Death Certificate Database, Office of Vital Records and Statistics, Utah Department of Health and Human Services
- Population Estimates for 1999 and earlier: Utah Governor's Office of Planning and Budget
- Population Estimates for 2000-2019: National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) through a collaborative agreement with the U.S. Census Bureau, IBIS Version 2020
- For years 2020 and later, the population estimates are provided by the Kem C. Gardner Policy Institute, Utah state and county annual population estimates are by single year of age and sex, IBIS Version 2022
- National Vital Statistics System, National Center for Health Statistics, U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
