Complete Health Indicator Report of Diabetes Prevalence
Definition
Percentage of Utah adults (18+) diagnosed with diabetes.Numerator
Number of Utah adults who reported being told by a healthcare professional that they have diabetes (excludes women who were told they had diabetes only during pregnancy or those who reported they had "borderline" or prediabetes).Denominator
Utah adults 18 and over.Data Interpretation Issues
The Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) is the primary source for estimating diabetes prevalence for Utah. The BRFSS is a telephone survey (with interviews using both landline and cell phones) that includes only adults 18 and over.Why Is This Important?
More than 191,000 Utah adults have been diagnosed with diabetes. Diabetes is a disease that can have devastating consequences. It is the leading cause of non-traumatic lower-extremity amputation and kidney failure. It is also the leading cause of blindness among adults younger than 75. It is one of the leading causes of heart disease. Diabetes places an enormous burden on healthcare resources. Nationally, approximately $412.9 billion is spent annually: $306.6 billion in direct medical costs and $106.3 billion in indirect medical costs (disability, work loss, and premature death; see [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37909353/ Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2022]. In Utah, more than a billion dollars each year is spent on direct and indirect medical costs of diabetes. Currently, about 98 million Americans aged 18 and older have prediabetes, a condition that puts them at high risk for developing diabetes. For many individuals, taking small steps, such as losing 5-7% of their weight or increasing physical activity, can help them delay or prevent developing diabetes.Other Objectives
Healthy People 2030 (HP 2030) emphasizes reducing the incidence of diabetes. HP 2030 Objective D-01 is "Reduce the number of diabetes cases diagnosed yearly."How Are We Doing?
The rising prevalence of diabetes in Utah appears to be slowing. However, many Utah adults are overweight or obese, and/or lead sedentary lifestyles, adding to the number of people at risk for developing diabetes. Prediabetes is a condition in which blood sugar rates are elevated but not yet high enough to reach the clinical threshold of a diabetes diagnosis. An estimated 97.6 million Americans age 18 and older have prediabetes. Unless those individuals take steps to reduce their risk of diabetes, such as increasing physical activity, eating a more nutritious diet, or losing weight, the majority will have diabetes within 10 years.How Do We Compare With the U.S.?
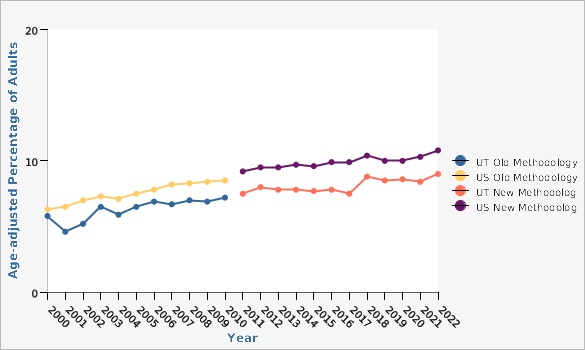
According to the 2022 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS), Utah's age-adjusted rate of diabetes is 9.0% of adults, compared to the U.S. age-adjusted rate of 10.8%. (Note: An age-adjusted rate is an artificial rate that "adjusts" for differences in age distributions between populations).What Is Being Done?
The Healthy Environments Active Living (HEAL) program encourages people with diabetes to enroll in a Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support (DSMES) class. These classes have been shown to help individuals develop the skills they need to manage their diabetes and are usually taught by registered dietitians, registered nurses, or pharmacists, who may also hold the status of Certified Diabetes Care and Education Specialists (CDCES). CDCES have considerable expertise in diabetes management and understand what the individual with diabetes is going through. The Utah Healthy Aging Program supports Chronic Disease Self-Management programs and Diabetes Self-Management programs throughout the state, this program is also called the Living Well with Chronic Conditions program. This 6-week program is available throughout the state at no cost and taught by community members. Information is available from Nichole Shepard, 385-315-2000, nshepard@utah.gov. More information is available on the [https://healthyaging.utah.gov/ Healthy Aging Program website]. The HEAL program is working statewide to increase the number of locations that offer DSMES and also promote DSMES to eligible participants. The National Diabetes Prevention Program (National DPP) is an evidence-based program to prevent type 2 diabetes. The HEAL program works with statewide partners to promote the National DPP to eligible Utahns and also is working to expand National DPP sites across the state.Evidence-based Practices
Diabetes Self-Management classes have been shown to improve blood sugar control among participants. In Utah, programs are available that are recognized by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) or certified by the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists (ADCES). Information on classes in Utah is available on the [https://heal.health.utah.gov/dsmes-programs/ HEAL website].Available Services
The American Diabetes Association is an excellent resource for all types of information on diabetes. Call 1-800-DIABETES or visit the [https://diabetes.org/ website]. [https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/community-health-outreach/information-clearinghouses?dkrd=hisce0003 The National Diabetes Education Program] has resources for diabetes management for professionals, businesses, and patients. Most materials are available upon request at no charge. [https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/prevention/index.html The National Diabetes Prevention Program] has resources for diabetes prevention for employers, insurers, health care professionals, program providers, and individuals. [https://dhhs.utah.gov/ The Utah Department of Health and Human Services] has a Health Resource hotline: 1-888- 222-2542. Please call this number or 211 for information about self-management programs in Utah. [https://www.diabeteseducator.org/ Association of Diabetes Care and Educational Specialists] 800-338-3633 [https://www.heart.org/ American Heart Association][[br]] 1937 S. 300 W. #120[[br]] Salt Lake City, UT 84115 [[br]] (801) 484-3838 or 1-800-242-8721Health Program Information
The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Resource hotline can provide information about enrolling in diabetes self-management classes. Call 1-888-222-2542 or 211 for more information. The Utah Department of Health and Human Services Healthy Environments Active Living (HEAL) program plays a key role in improving the health of residents in the state of Utah. The program was formed in July 2013 (as EPICC), through a new funding opportunity from the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that allowed for the merging of three previously existing programs: the Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Program, the Diabetes Prevention and Control Program, and the Physical Activity, Nutrition and Obesity Program, as well as the addition of a school health program. The Healthy Environments Active Living Program (HEAL) was recently restructured as part of this strategic planning process and the new program model focuses on working together with staff and partners to address the social determinants of health while advancing health equity and increasing policy, systems and environment changes. HEAL champions public health initiatives and addresses the challenges of making health awareness and access truly universal and equitable in eight key areas: nutrition, heart health, diabetes, physical activity, schools, child care, community health workers, and worksites. Visit [https://heal.health.utah.gov/ HEAL's website] for more information.Related Indicators
Relevant Population Characteristics
Anyone can develop diabetes, but the risk for developing type 2 diabetes is greater for those who are older, overweight or obese, physically inactive, and/or a member of a minority racial or ethnic group. As the Utah population ages, and as the proportion of high-risk minority ethnic and racial groups in the population increases, a greater percentage of Utahns will be at risk for developing diabetes. There is considerable variation in prevalence by race and ethnicity. According to a CDC report on diabetes in the U.S., 7.4% of non-Hispanic White persons aged 18 or older have diabetes (age-adjusted prevalence). Members of the American Indian/Alaskan Native population are more than twice as likely to have diabetes as non-Hispanic White persons; 15.1% of people in this group have been diagnosed. High prevalence is also seen in the non-Hispanic Black population, where the percentage diagnosed is 12.7% among adults aged 18 and over. High prevalence is also seen in the non-Hispanic Black population, where 12.1% of Hispanics aged 18 and older have diagnosed diabetes. Among non-Hispanic Asians aged 18 and older the age-adjusted rate of diagnosed diabetes is 8.0%. (See [https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf ''National Diabetes Statistics Report, 2020'']).Related Relevant Population Characteristics Indicators:
- Utah Population Characteristics: Age Distribution of the Population
- Utah Population Characteristics: Education Level in the Population
- Utah Population Characteristics: Household Income
- Utah Health Improvement Index (HII)
- Utah Population Characteristics: Poverty, All Persons
- Utah Population Characteristics: Racial and Ethnic Composition of the Population
Health Care System Factors
Screening for diabetes is generally recommended for people aged 45 and over, although those with a high risk of developing diabetes (e.g., overweight, member of minority racial or ethnic group) may wish to consider screening by age 30, or even earlier. Testing for diabetes is generally covered by insurance. For those without insurance, the American Diabetes Association may be contacted about the availability of low-cost or free screening (801-363-3024). In 2022, the estimated total cost for diabetes in the U.S. was $412.9 billion. Even undiagnosed diabetes can burden the healthcare system. Undiagnosed diabetes costs the nation about $31.7 billion a year. Prediabetes is estimated to cost $43.4 billion (See [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37909353/ ''Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2022''], [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6702611/#:~:text=Undiagnosed%20diabetes%20(7.9%25%2C%20%2431.7,%24403.9%20billion%20annually%20(10). "Understanding the economic costs of diabetes and prediabetes and what we may learn about reducing the health and economic burden of these conditions"]).Related Health Care System Factors Indicators:
Risk Factors
Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for developing diabetes. The risk of developing diabetes can be substantially reduced through weight loss and regular physical activity. The Diabetes Primary Prevention Study showed that weight loss and participation in regular physical activity can significantly decrease the risk. The clinical trial included over 3,000 people who had impaired fasting glucose and were at an increased risk for developing diabetes. Participants who engaged in moderately intense physical activity for 30 minutes per day and lost 5 to 7 percent of their body weight decreased their risk of diabetes dramatically. This behavioral activity was effective for all participants in the study, regardless of age or ethnic group (see [https://www.niddk.nih.gov/about-niddk/research-areas/diabetes/diabetes-prevention-program-dpp?dkrd=prspt1922 Diabetes Prevention Program, NIH]). Some risk factors cannot be modified, such as older age or membership in a minority racial or ethnic group. Nevertheless, risk can be substantially reduced through adhering to a nutritious diet and participating in regular physical activity.Related Risk Factors Indicators:
Health Status Outcomes
Diabetes can have serious consequences. It is the leading cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations, and is also the leading cause of blindness among working-age adults. It is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and end-stage renal disease.Related Health Status Outcomes Indicators:
Graphical Data Views
The 2022 age-adjusted rate of diabetes for Utah (9.0%) was lower than the rate for the U.S. (10.8%).
| BRFSS Utah vs. U.S. | Year | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 48 | ||||||
| UT Old Methodology | 2000 | 5.8% | 4.6% | 7.0% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2001 | 4.6% | 3.7% | 5.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2002 | 5.2% | 4.3% | 6.1% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2003 | 6.5% | 5.5% | 7.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2004 | 5.9% | 5.2% | 6.7% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2005 | 6.5% | 5.7% | 7.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2006 | 6.9% | 6.1% | 7.8% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2007 | 6.7% | 6.0% | 7.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2008 | 7.0% | 6.3% | 7.7% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2009 | 6.9% | 6.4% | 7.4% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2010 | 7.2% | 6.7% | 7.8% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2000 | 6.3% | 6.1% | 6.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2001 | 6.5% | 6.3% | 6.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2002 | 7.0% | 6.8% | 7.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2003 | 7.3% | 7.1% | 7.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2004 | 7.1% | 6.9% | 7.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2005 | 7.5% | 7.4% | 7.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2006 | 7.8% | 7.6% | 7.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2007 | 8.2% | 8.0% | 8.3% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2008 | 8.3% | 8.2% | 8.5% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2009 | 8.4% | 8.4% | 8.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2010 | 8.5% | 8.3% | 8.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2011 | 7.5% | 7.0% | 8.0% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2012 | 8.0% | 7.5% | 8.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2013 | 7.8% | 7.3% | 8.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2014 | 7.8% | 7.3% | 8.3% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2015 | 7.7% | 7.1% | 8.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2016 | 7.8% | 7.2% | 8.4% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2017 | 7.5% | 6.9% | 8.1% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2018 | 8.8% | 8.2% | 9.5% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2019 | 8.5% | 7.9% | 9.1% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2020 | 8.6% | 8.0% | 9.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2021 | 8.4% | 7.8% | 9.0% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2022 | 9.0% | 8.4% | 9.7% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2011 | 9.2% | 9.1% | 9.4% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2012 | 9.5% | 9.4% | 9.7% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2013 | 9.5% | 9.4% | 9.7% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2014 | 9.7% | 9.6% | 9.9% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2015 | 9.6% | 9.5% | 9.8% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2016 | 9.9% | 9.7% | 10.0% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2017 | 9.9% | 9.7% | 10.1% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2018 | 10.4% | 10.2% | 10.6% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2019 | 10.0% | 9.8% | 10.2% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2020 | 10.0% | 9.8% | 10.2% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2021 | 10.3% | 10.1% | 10.5% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2022 | 10.8% | 10.6% | 11.0% | ||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]] [[br]] Rates are age-adjusted using 5 age groups. Beginning in 2011, U.S. BRFSS data include both landline and cell phone respondent data along with a new weighting methodology called iterative proportional fitting, or raking. Utah changed to the new methodology in 2009. This new methodology utilizes additional demographic information (such as education, race, and marital status) in the weighting procedure. More details about these changes can be found at: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/pdf/opha/resource/brfss/RakingImpact2011.pdf].Data Sources
- Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]
- Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey Data, US Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
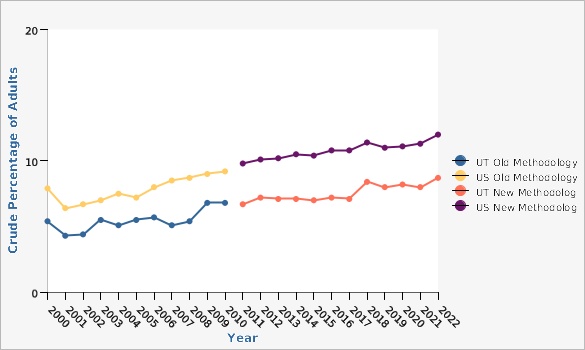
Rates for diabetes prevalence among Utah adults have been fairly stable for years 2009-2017, and 2018-2022.
| BRFSS Utah vs. U.S. | Year | Crude Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 46 | ||||||
| UT Old Methodology | 2000 | 5.4% | 4.3% | 6.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2001 | 4.3% | 3.4% | 5.1% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2002 | 4.4% | 3.5% | 5.2% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2003 | 5.5% | 4.6% | 6.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2004 | 5.1% | 4.4% | 5.8% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2005 | 5.5% | 4.9% | 6.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2006 | 5.7% | 5.1% | 6.5% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2007 | 5.1% | 6.6% | 6.7% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2008 | 5.4% | 6.8% | 5.8% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2009 | 6.8% | 6.2% | 7.3% | ||
| UT Old Methodology | 2010 | 6.8% | 6.3% | 7.4% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2000 | 7.9% | 7.8% | 7.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2001 | 6.4% | 6.2% | 6.6% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2002 | 6.7% | 6.5% | 6.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2003 | 7.0% | 6.8% | 7.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2004 | 7.5% | 7.3% | 7.6% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2005 | 7.2% | 7.0% | 7.4% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2006 | 8.0% | 7.6% | 7.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2007 | 8.5% | 7.8% | 8.2% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2008 | 8.7% | 8.4% | 8.7% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2009 | 9.0% | 8.6% | 8.9% | ||
| US Old Methodology | 2010 | 9.2% | 8.9% | 9.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2011 | 6.7% | 6.2% | 7.2% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2012 | 7.2% | 6.7% | 7.7% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2013 | 7.1% | 6.6% | 7.7% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2014 | 7.1% | 6.7% | 7.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2015 | 7.0% | 6.5% | 7.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2016 | 7.2% | 6.7% | 7.8% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2017 | 7.1% | 6.5% | 7.7% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2018 | 8.4% | 7.8% | 9.0% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2019 | 8.0% | 7.5% | 8.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2020 | 8.2% | 7.6% | 8.9% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2021 | 8.0% | 7.4% | 8.6% | ||
| UT New Methodology | 2022 | 8.7% | 8.1% | 9.4% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2011 | 9.8% | 9.6% | 9.9% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2012 | 10.1% | 9.9% | 10.3% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2013 | 10.2% | 10.1% | 10.4% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2014 | 10.5% | 10.3% | 10.7% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2015 | 10.4% | 10.3% | 10.6% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2016 | 10.8% | 10.6% | 10.9% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2017 | 10.8% | 10.6% | 11.0% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2018 | 11.4% | 11.2% | 11.6% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2019 | 11.0% | 10.9% | 11.2% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2020 | 11.1% | 10.9% | 11.3% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2021 | 11.3% | 11.1% | 11.5% | ||
| US New Methodology | 2022 | 12.0% | 11.8% | 12.2% | ||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]] [[br]] This graph demonstrates the difference in prevalence using old and new methodologies. Beginning in 2011, U.S. BRFSS data include both landline and cell phone respondent data along with a new weighting methodology called iterative proportional fitting, or raking. Utah changed to the new methodology in 2009. The new methodology utilizes additional demographic information (such as education, race, and marital status) in the weighting procedure. Both of these methodology changes were implemented to account for an increased number of U.S. households without landline phones and an under-representation of certain demographic groups that were not well-represented in the sample. More details about these changes can be found at: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/pdf/opha/resource/brfss/RakingImpact2011.pdf].Data Sources
- Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]
- Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey Data, US Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
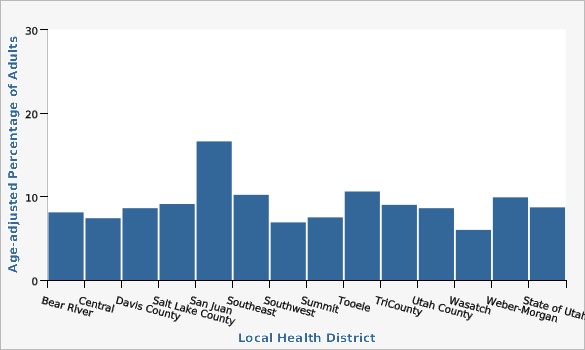
Southwest and Wasatch County local health districts had a lower rate than the state. San Juan Local Health District had a rate that was higher than the state.
The overall age-adjusted rate for the state was 8.7%.
| Local Health District | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 14 | ||||||
| Bear River | 8.1% | 6.5% | 10.1% | |||
| Central | 7.4% | 5.8% | 9.5% | |||
| Davis County | 8.6% | 7.3% | 10.1% | |||
| Salt Lake County | 9.1% | 8.3% | 10.0% | |||
| San Juan | 16.6% | 11.6% | 23.0% | |||
| Southeast | 10.2% | 7.8% | 13.2% | |||
| Southwest | 6.9% | 5.7% | 8.4% | |||
| Summit | 7.5% | 5.1% | 10.8% | |||
| Tooele | 10.6% | 8.6% | 13.0% | |||
| TriCounty | 9.0% | 7.2% | 11.1% | |||
| Utah County | 8.6% | 7.6% | 9.6% | |||
| Wasatch | 6.0% | 4.2% | 8.5% | |||
| Weber-Morgan | 9.9% | 8.4% | 11.6% | |||
| State of Utah | 8.7% | 8.3% | 9.2% | |||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]] [[br]] Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]Five years of data were combined to improve reliability of the estimates. However, some estimates still did not meet DHHS standards for reliability and should be interpreted with caution. Those particular estimates are indicated in the data table.
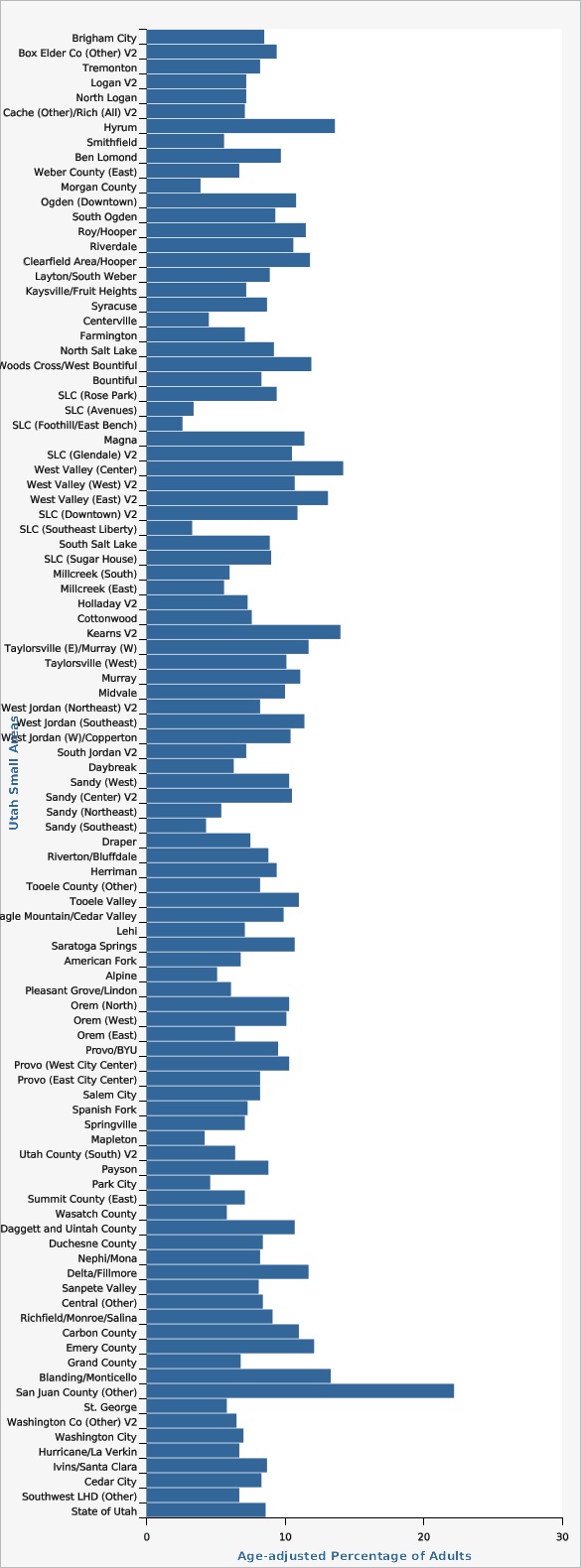
Several Utah Small Areas had rates statistically significantly higher than the state rate: Roy/Hooper, Clearfield Area/Hooper, West Valley (Center), West Valley (East) V2, Kearns V2, Taylorsville (East)/Murray (West), West Jordan (Southeast), Tooele Valley, Daggett and Uintah County, Carbon County, Emery County, Blanding/Monticello, and San Juan (Other).
Utah Small Areas with statistically significantly lower rates than the state rate were: Morgan County, Salt Lake City (Avenues), Salt Lake City (Foothill/East Bench), Salt Lake City (Southeast Liberty), Sandy (Southeast), Pleasant Grove/Lindon, Mapleton, Park City, Wasatch County, and St. George.
| Utah Small Areas | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Note | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 100 | ||||||
| Brigham City | 8.5% | 6.4% | 11.4% | |||
| Box Elder Co (Other) V2 | 9.4% | 5.7% | 15.0% | |||
| Tremonton | 8.2% | 5.4% | 12.1% | |||
| Logan V2 | 7.2% | 5.5% | 9.5% | |||
| North Logan | 7.2% | 4.6% | 11.3% | |||
| Cache (Other)/Rich (All) V2 | 7.1% | 5.2% | 9.5% | |||
| Hyrum | 13.6% | 8.2% | 21.7% | |||
| Smithfield | 5.6% | 3.5% | 8.9% | |||
| Ben Lomond | 9.7% | 7.8% | 12.0% | |||
| Weber County (East) | 6.7% | 5.1% | 8.8% | |||
| Morgan County | 3.9% | 2.1% | 7.2% | Estimate may be unreliable. | ||
| Ogden (Downtown) | 10.8% | 8.3% | 13.9% | |||
| South Ogden | 9.3% | 6.9% | 12.5% | |||
| Roy/Hooper | 11.5% | 9.1% | 14.4% | |||
| Riverdale | 10.6% | 7.7% | 14.6% | |||
| Clearfield Area/Hooper | 11.8% | 9.6% | 14.5% | |||
| Layton/South Weber | 8.9% | 7.3% | 10.8% | |||
| Kaysville/Fruit Heights | 7.2% | 5.3% | 9.7% | |||
| Syracuse | 8.7% | 6.1% | 12.1% | |||
| Centerville | 4.5% | 2.3% | 8.7% | Estimate may be unreliable. | ||
| Farmington | 7.1% | 4.8% | 10.2% | |||
| North Salt Lake | 9.2% | 5.8% | 14.4% | |||
| Woods Cross/West Bountiful | 11.9% | 7.9% | 17.6% | |||
| Bountiful | 8.3% | 6.5% | 10.4% | |||
| SLC (Rose Park) | 9.4% | 6.7% | 13.1% | |||
| SLC (Avenues) | 3.4% | 1.9% | 6.0% | |||
| SLC (Foothill/East Bench) | 2.6% | 1.5% | 4.7% | Estimate may be unreliable. | ||
| Magna | 11.4% | 8.4% | 15.4% | |||
| SLC (Glendale) V2 | 10.5% | 6.5% | 16.6% | |||
| West Valley (Center) | 14.2% | 11.2% | 17.9% | |||
| West Valley (West) V2 | 10.7% | 7.9% | 14.4% | |||
| West Valley (East) V2 | 13.1% | 10.2% | 16.8% | |||
| SLC (Downtown) V2 | 10.9% | 7.7% | 15.3% | |||
| SLC (Southeast Liberty) | 3.3% | 1.8% | 5.9% | Estimate may be unreliable. | ||
| South Salt Lake | 8.9% | 6.0% | 13.1% | |||
| SLC (Sugar House) | 9.0% | 6.5% | 12.2% | |||
| Millcreek (South) | 6.0% | 3.9% | 9.1% | |||
| Millcreek (East) | 5.6% | 3.4% | 8.9% | |||
| Holladay V2 | 7.3% | 4.7% | 11.2% | |||
| Cottonwood | 7.6% | 5.3% | 10.7% | |||
| Kearns V2 | 14.0% | 10.7% | 18.1% | |||
| Taylorsville (E)/Murray (W) | 11.7% | 8.9% | 15.1% | |||
| Taylorsville (West) | 10.1% | 7.6% | 13.4% | |||
| Murray | 11.1% | 8.0% | 15.1% | |||
| Midvale | 10.0% | 7.3% | 13.5% | |||
| West Jordan (Northeast) V2 | 8.2% | 5.8% | 11.6% | |||
| West Jordan (Southeast) | 11.4% | 8.7% | 14.8% | |||
| West Jordan (W)/Copperton | 10.4% | 7.4% | 14.4% | |||
| South Jordan V2 | 7.2% | 5.3% | 9.6% | |||
| Daybreak | 6.3% | 4.2% | 9.3% | |||
| Sandy (West) | 10.3% | 7.4% | 14.3% | |||
| Sandy (Center) V2 | 10.5% | 7.3% | 14.7% | |||
| Sandy (Northeast) | 5.4% | 3.3% | 8.9% | |||
| Sandy (Southeast) | 4.3% | 3.1% | 6.0% | |||
| Draper | 7.5% | 5.2% | 10.5% | |||
| Riverton/Bluffdale | 8.8% | 6.6% | 11.6% | |||
| Herriman | 9.4% | 6.9% | 12.6% | |||
| Tooele County (Other) | 8.2% | 6.2% | 10.8% | |||
| Tooele Valley | 11.0% | 9.3% | 12.8% | |||
| Eagle Mountain/Cedar Valley | 9.9% | 6.8% | 14.1% | |||
| Lehi | 7.1% | 5.4% | 9.4% | |||
| Saratoga Springs | 10.7% | 7.3% | 15.4% | |||
| American Fork | 6.8% | 5.0% | 9.0% | |||
| Alpine | 5.1% | 2.8% | 9.1% | Estimate may be unreliable. | ||
| Pleasant Grove/Lindon | 6.1% | 4.8% | 7.8% | |||
| Orem (North) | 10.3% | 8.0% | 13.1% | |||
| Orem (West) | 10.1% | 7.3% | 13.8% | |||
| Orem (East) | 6.4% | 4.4% | 9.1% | |||
| Provo/BYU | 9.5% | 7.1% | 12.6% | |||
| Provo (West City Center) | 10.3% | 7.4% | 12.6% | |||
| Provo (East City Center) | 8.2% | 4.6% | 14.2% | |||
| Salem City | 8.2% | 5.2% | 12.5% | |||
| Spanish Fork | 7.3% | 5.6% | 9.5% | |||
| Springville | 7.1% | 5.1% | 9.7% | |||
| Mapleton | 4.2% | 2.4% | 7.4% | |||
| Utah County (South) V2 | 6.4% | 3.9% | 10.6% | |||
| Payson | 8.8% | 6.4% | 11.9% | |||
| Park City | 4.6% | 3.0% | 7.0% | |||
| Summit County (East) | 7.1% | 5.1% | 9.9% | |||
| Wasatch County | 5.8% | 4.5% | 7.3% | |||
| Daggett and Uintah County | 10.7% | 9.1% | 12.5% | |||
| Duchesne County | 8.4% | 6.7% | 10.3% | |||
| Nephi/Mona | 8.2% | 5.3% | 12.5% | |||
| Delta/Fillmore | 11.7% | 8.5% | 15.9% | |||
| Sanpete Valley | 8.1% | 5.8% | 11.2% | |||
| Central (Other) | 8.4% | 6.7% | 10.5% | |||
| Richfield/Monroe/Salina | 9.1% | 6.7% | 12.4% | |||
| Carbon County | 11.0% | 8.8% | 13.6% | |||
| Emery County | 12.1% | 9.4% | 15.5% | |||
| Grand County | 6.8% | 4.4% | 10.6% | |||
| Blanding/Monticello | 13.3% | 9.2% | 18.8% | |||
| San Juan County (Other) | 22.2% | 16.2% | 29.7% | |||
| St. George | 5.8% | 4.6% | 7.2% | |||
| Washington Co (Other) V2 | 6.5% | 3.8% | 10.9% | |||
| Washington City | 7.0% | 4.6% | 10.4% | |||
| Hurricane/La Verkin | 6.7% | 4.8% | 9.3% | |||
| Ivins/Santa Clara | 8.7% | 5.8% | 12.8% | |||
| Cedar City | 8.3% | 6.3% | 10.8% | |||
| Southwest LHD (Other) | 6.7% | 4.8% | 9.1% | |||
| State of Utah | 8.6% | 8.4% | 8.9% | |||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]][[br]]Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.[[br]] [[br]] A description of the Utah Small Areas may be found on the Methodology and Guidelines page: [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/resource/Guidelines.html].Data Source
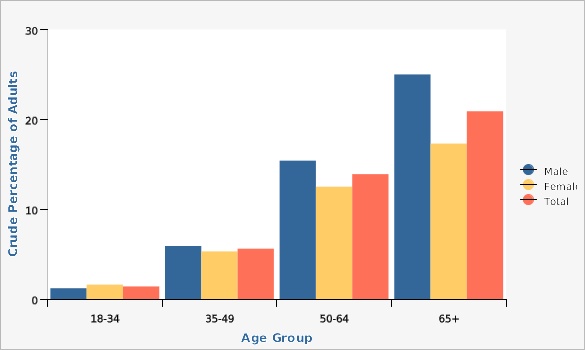
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]For both males and females, the highest rates of diabetes were observed for adults aged 65 and over.
| Males vs. Females | Age Group | Crude Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 12 | ||||||
| Male | 18-34 | 1.2% | 0.8% | 1.8% | ||
| Male | 35-49 | 5.9% | 4.9% | 7.2% | ||
| Male | 50-64 | 15.4% | 13.7% | 17.4% | ||
| Male | 65+ | 25.0% | 22.8% | 27.2% | ||
| Female | 18-34 | 1.6% | 1.1% | 2.4% | ||
| Female | 35-49 | 5.3% | 4.3% | 6.5% | ||
| Female | 50-64 | 12.5% | 10.8% | 14.3% | ||
| Female | 65+ | 17.3% | 15.7% | 19.1% | ||
| Total | 18-34 | 1.4% | 1.1% | 1.8% | ||
| Total | 35-49 | 5.6% | 4.9% | 6.5% | ||
| Total | 50-64 | 13.9% | 12.7% | 15.3% | ||
| Total | 65+ | 20.9% | 19.5% | 22.3% | ||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change.Data Source
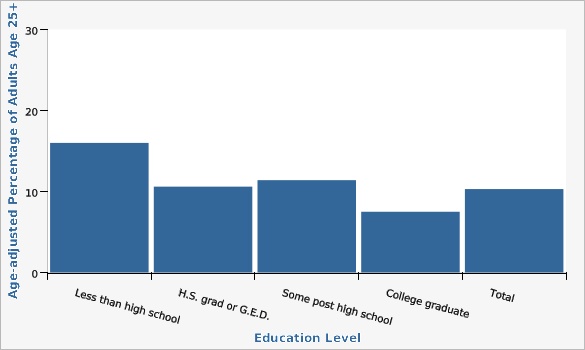
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]The overall percentage for adults age 25+ with diabetes for all education levels was 10.3%. Adults with a college graduate degree had the lowest rate of diabetes, 7.5%, which was statistically significant.
| Education Level | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults Age 25+ | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| Less than high school | 16.0% | 12.5% | 20.4% | |||
| H.S. grad or G.E.D. | 10.6% | 9.2% | 12.3% | |||
| Some post high school | 11.4% | 10.0% | 13.0% | |||
| College graduate | 7.5% | 6.6% | 8.5% | |||
| Total | 10.3% | 9.5% | 11.1% | |||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]][[br]]Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
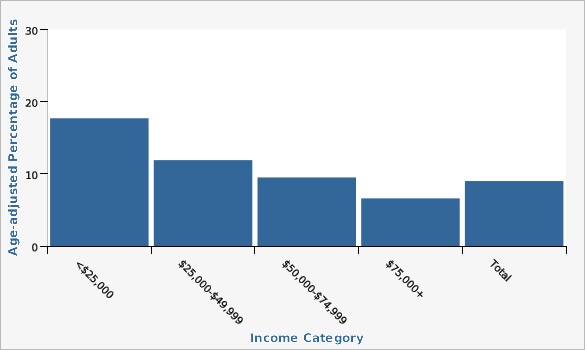
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]The age-adjusted diabetes rate for adults with incomes between $0-$24,999 and $25,000-$49,999 was higher than the state rate of 9.0%.
| Income Category | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 5 | ||||||
| <$25,000 | 17.7% | 14.5% | 21.6% | |||
| $25,000-$49,999 | 11.9% | 10.0% | 14.2% | |||
| $50,000-$74,999 | 9.5% | 7.7% | 11.6% | |||
| $75,000+ | 6.6% | 5.7% | 7.6% | |||
| Total | 9.0% | 8.4% | 9.7% | |||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]][[br]]Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population.Data Source
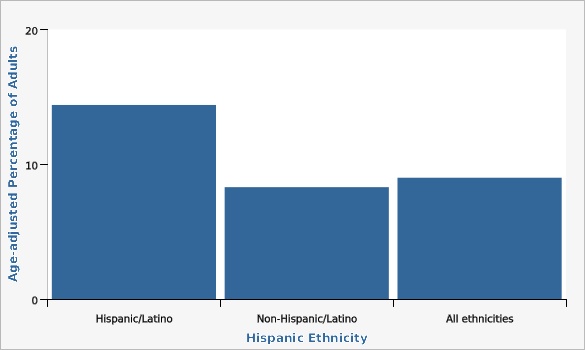
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]In 2022, there was a significantly higher rate of diabetes among the Hispanic population versus the non-Hispanic population.
| Hispanic Ethnicity | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 3 | ||||||
| Hispanic/Latino | 14.4% | 11.8% | 17.4% | |||
| Non-Hispanic/Latino | 8.3% | 7.6% | 9.0% | |||
| All ethnicities | 9.0% | 8.4% | 9.7% | |||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]][[br]]Rates are age-adjusted and standardized to the U.S. 2000 population.Data Source
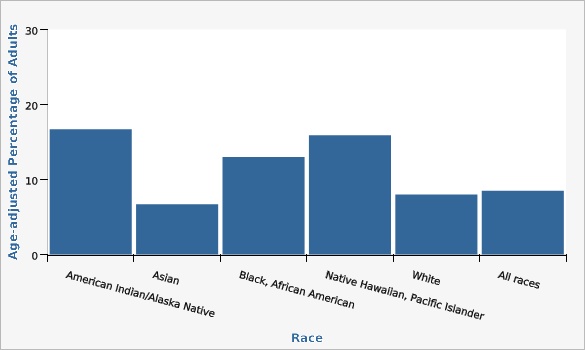
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]Three years of data (2020-2022) were combined to obtain reliable estimates. Prevalence of diabetes is especially high for people who identify as American Indian/Alaska Native, Black, and Pacific Islander.
It is important to note that these rates are age-adjusted, meaning that rates are artificially compared as though the age distribution for all populations were the same.
| Race | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 6 | ||||||
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 16.7% | 12.7% | 21.6% | |||
| Asian | 6.7% | 4.4% | 10.2% | |||
| Black, African American | 13.0% | 9.2% | 18.0% | |||
| Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islander | 15.9% | 9.9% | 24.5% | |||
| White | 8.0% | 7.6% | 8.3% | |||
| All races | 8.5% | 8.2% | 8.9% | |||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]][[br]]Age-adjusted to U.S. 2000 standard population based on 3 age groups: 18-34, 35-49, and 50+.Data Source
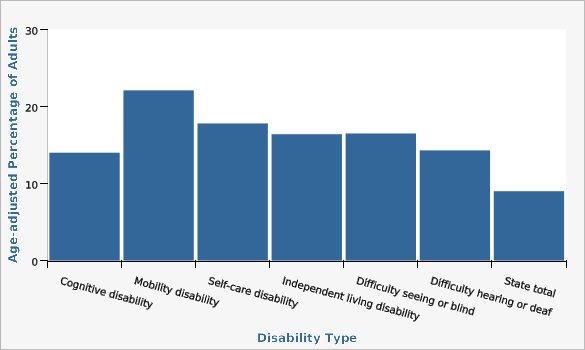
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]In 2022, there were no significant differences of diabetes percentages by type of disability; however, all disabilities had a significantly higher rate of diabetes than the state (9.0%).
| Disability Type | Age-adjusted Percentage of Adults | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Record Count: 7 | ||||||
| Cognitive disability | 14.0% | 11.4% | 17.0% | |||
| Mobility disability | 22.1% | 18.4% | 26.3% | |||
| Self-care disability | 17.8% | 12.9% | 24.1% | |||
| Independent living disability | 16.4% | 13.0% | 20.5% | |||
| Difficulty seeing or blind | 16.5% | 11.8% | 22.6% | |||
| Difficulty hearing or deaf | 14.3% | 10.8% | 18.7% | |||
| State total | 9.0% | 8.4% | 9.7% | |||
Data Notes
"Don't know" and "Refused" responses were eliminated from the denominator. In 2016, Utah BRFSS modified its methodology for age adjustment for increased precision. With this change Utah is consistent with both the U.S. and other states using IBIS. Data has been updated from 2011 onward in all chart views to reflect this change. [[br]][[br]]Rates are age-adjusted and standardized to the U.S. 2000 population.Data Source
Utah Department of Health and Human Services Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) [https://ibis.health.utah.gov/ibisph-view/query/selection/brfss/BRFSSSelection.html]References and Community Resources
[http://www.diabetes.org American Diabetes Association] Much of the information for this indicator was taken from the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Prevention Program [https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes?dkrd=lgdmn0026 National Diabetes Information Clearinghouse] [http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes Division of Diabetes Translation, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention] [http://www.diabeteseducator.org American Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists] Information on registering for self-management prediabetes and diabetes programs can be found [http://livingwell.utah.gov/index.php here].More Resources and Links
Evidence-based community health improvement ideas and interventions may be found at the following sites:- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) WONDER Database, a system for disseminating public health data and information.
- United States Census Bureau data dashboard.
- Utah healthy Places Index, evidence-based and peer-reviewed tool, supports efforts to prioritize equitable community investments, develop critical programs and policies across the state, and much more.
- County Health Rankings
- Kaiser Family Foundation's StateHealthFacts.org
- Medical literature can be queried at PubMed library.
Page Content Updated On 03/04/2024,
Published on 03/28/2024